Strategic Frameworks for Information Technology
advertisement

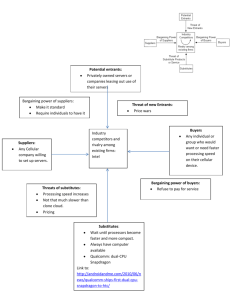
Strategic Frameworks for Project Justification PSC 5170 Organization Goals Business Vision Mission Objective Tactic = Business Justification IS Vision Mission Objective Tactic = Project Contribution Roles Sponsor: funds and champions the project in the organization Client: reviews the project milestones and decision points from the business point of vies User: works with the system on a regular basis Strategic Information Systems IS that help gain strategic advantage Significantly change manner in which business supported by the system is done Outwardly aimed at direct competition Inwardly focus on enhancing the competitive position Create strategic alliances Value Chain Model Chain of basic activities that add to firm’s products or services Primary activities Secondary activities Value Chain Value Chain Primary Activities Inbound Outbound Operations Marketing and Sales After-Sale Services Value Chain Support Activities Technology development Procurement Human Resources Management Management Control accounting/finance coordination general management central planning Porter’s Competitive Forces Model The model recognizes five major forces that could endanger a company’s position in a given industry. The The The The The threat of entry of new competitors bargaining power of suppliers bargaining power of customers (buyers) threat of substitute products or services rivalry among existing firms in the industry External Competitive Forces Competitive Forces Threat of entry of new competition Bargaining power of suppliers Bargaining power of buyers Threat of substitute products or services Rivalry among existing firms Strategies for Competitive Forces Note - strength of force is determined by factors in industry Gain a competitive edge Build defenses against forces Formulate actions to influence forces Three Generic Strategies Cost leadership (lowest cost in industry) Differentiation (of products/services/quality) Focus (finding a specialized niche) Be Low Cost Producer IT strategic if it can: Help reduce production costs & clerical work Reduce inventory, accounts receivable, etc. Use facilities and materials better Offer interorganizational efficiencies Produce Unique Product - IT strategic if it can: Offer significant component of product Offer key aspect of value chain Permit product customization to meet customer’s unique needs Provide higher/unique level of customer service/satisfaction Fill Market Niche - IT strategic if it can: Permit identification of special needs of unique target market Spot and respond to unusual trends Strategic Questions Can IT create barriers to entry? (new entrants) Can IT build in switching costs? (buyers) Can IT strengthen customer relationships? (buyers) Strategic Questions (cont) Can IT change the balance of power in supplier relationships? (suppliers) Can IT change the basis of competition? (competitors) Can IT generate new products?(competitors, substitutes) Risks of IS Success Change the Basis of Competition Lower Entry Barriers Promote Litigation or Regulation Awake Sleeping Giant Reflect Bad Timing Are Too Advanced Transformational Information Systems Radical changes in an organization’s business processes Radical changes in an organization’s structure Radical changes in an industry’s value streams Business Process Reengineering (BPR) Completely changes manner in which business is done Fewer steps, shorter cycle times Complete, more expert handling of events Not incremental improvement Typically uses IT as an enabler Involves discontinuous thinking Characteristics of BPR Combining jobs Empowering employees Jobs done simultaneously Customizing product/service Work performed where most logical Single point of customer contact Transformational Information Systems Radical changes in an organization’s structure reduce layers of management empower front-line workers loosely couple work units Radical changes in an industry’s value streams disintermediation creating new markets