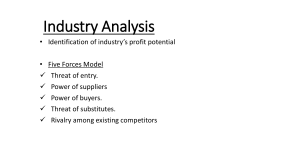
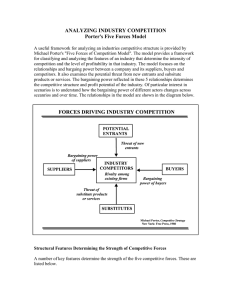
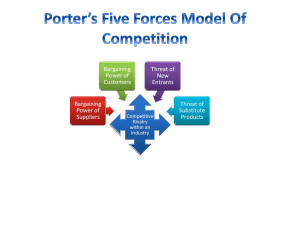
Customers & competitors FIRM' S INDUSTRY First strategic deicision Vulnerably to UNSEEN competitors Not obvious! Start: customer oriented view (no based on the product offered) Fragmented industry NUMEBER/SIZE COMPETITORS SAME SIZES DIFFERENTIATED: loyalty STANDARD PRODUCTS STANDARDIZE: sales, rebates Buyer power Supplier power LOW SWITCHING COSTS New entrants RIVALRY aka WAR substitutes Promotions, discounts, price wars SLOW GROWTH IN DEMAND To use more: drop prices UNUSED CAPACITY FIXED COSTS , PERISHABLE PRODUCTS, HIGH STORAGE COSTS Steep discounts Investment in special equipment HIGH EXIT BARRIERS Labor or gov agreements Emotional ties Buyers' switching costs Buyer Demand BARGAINING POWER Concentration/size of BUYERS BACKWARD INTEGRATION B are struggling financially BUYER POWER : lower prices/ better quality Product is a significant proportion of buyer''s costs PRICE SENSITIVITY: the more, the more power . Tend to increase when 5 FORCES:THREAT & OPPORTUNITIES STEPS: 1.SPECIFIC FACTORS STEP 2: STRENGTH OF EACH FORCE SHAPE the profit-making POTENTIAL of the average firm in an industry Large volumes purchase Doesn't affect buyers' performance Doesn't save buyers money NUMBER SUPPLIER POWER SIZE FORWARD INTEGRATION Ex. Google in smartphones BARRIERS TO ENTRY signalling EXPERIENCE ECONOMIES LEARNING SCALE Patents & proprietary technology Better locations COST ADVANTAGES THREAT: NEW ENTRANTS EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT Ec. Of scope ( bundling) ANXIOUS TO GAIN MARKET SHARE & BRING NEW PRODUCTION CAPACITY Preferential access to CRITICAL RESOURCES CAPITAL REQUIREMENTS NETWORK EFFECTS The higher the start up costs, the lower entrants Firms that already spent on R&D in similar products Increases the SWITCHING COSTS for customers Restrict the market GOV. POLICY RESTRICTIONS RIVALRY ≠ SUBSTITUTE THREAT: SUBSTITUTIONS DOWNWARD PRESSURE on price AWARENESS & AVAILABILITY PRICE & PERFORMANCE Result of 5 forces analysis: industry's STRUCTURE and nature of competitive INTERACTION Rating HIGH or LOW on all forces is RARE 5 FORCES are subject to changes AVARAGE PROFITABILITY OF THE INDUSTRY INDUSTRY ATTRACTIVENESS STEP 2: ESTIMATE OVERALL ATTRACTIVENESS OF THE INDUSTRY POWER OVER BUYERS and SUPPLIERS ATTRACTIVE ones : firms have created BARRIERS TO ENTRY MINIMIZED THREAT OF SUBSTITUTES TRADITIONAL: 5 forcesmost attractive ones LIMITATION: executives have to choose markets BEFORE ENTERING Most attractive(5 forces prospective) is the LEAST ATTRACTIVE for new entrants TO enter you have to CIRCUMVENT BARRIERS TO ENTER NEW THINKING Where to compete DEPENDS ON THE UNIQUE VALUE THEY CAN OFFER (don't mimic incumbents) COMPLEMENTARY PRODUCTS AKA Ecosystems: products that can eb used in TANDEM with those of another industry NEW PRODUCTS/PROCESSES TECHNOLOGICAL CHANGE EARLY ADOPTERS: greater market share Can lower BARRIERS TO ENTRY INCREASE: customers income (LOW PRICE SENSITIVITY) and industry GROWTH RATE ECONOMIC GROWTH Changes in DEMAND for products (especially expensive items requiring LOANS) INTEREST RATES Impact the prices for IMPORTS EXCHANGE RATES GENERAL ENVIRONMENT EFFECTS ON PROFITABILITY DIFFICULT PLANNING THESE 3 CATEGORIES SHAPE AND CHANGE THE 5 FORCES FACTORS INFLATION ECONOMIC CONDITIONS macroeconomic forces DECREASE ECONOMIC GROWTH DEMOGRAPHIC FORCES INCREASE RIVALRY AND THREAT OF SUBSTITUTES Number of people,avg age, distribution, gender, ethnicity Shortages of key inputs ECOLOGICAL ENVIRONMENT Fluctuations in COST OF ENERGY GREEN INITIATIVES GLOBAL FORCES COMUNICATION & TRANSPORTATION TECHNOLOGIES POLITICAL, LEGAL, REGULATORY FORCES SOCIAL/CULTURAL FORCES (affect all the others) ECONOMIC GROWTH & RISING STANDARD OF LIVING OPPORTUNITIES & THREATS Society's cultural VALUES & NORMS FIRMS LOBBY GOV TO INFLUENCE THE LAWMAKERS RAISE COST OF ENTRY: licenses, insurances Less entrants