Chapter 2 --Market Imperfections and Value: Strategy Matters
advertisement

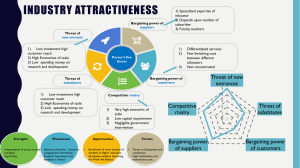
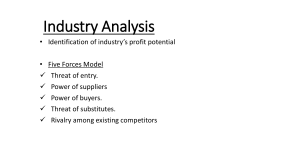
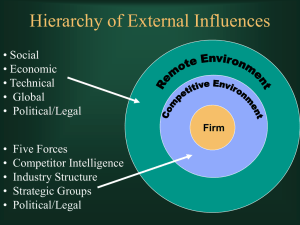
Chapter 2 --Market Imperfections and Value: Strategy Matters Conditions necessary for a perfectly competitive product market and resource market: No market power no producer is large enough to influence prices Identical product Identical cost No restrictions on entry or exit Complete information like information and expectations Sustainable Competitive Advantage Sustainable competitive advantage is the elimination of perfect competition for a sustainable period of time so as to provide economic profit Depends on: Industry characteristics Company actions Product features or cost advantages Assessing the Industry -Porter’s Five Forces Threat of new entries Bargaining power of buyers Bargaining power of suppliers Threat of substitutes Rivalry among existing firms Competitive Strategy. Free Press, 1980 Ways to Reduce the Threat of New Entries Economies of scale Patents, copyrights, & trade secrets Regulation Switching cost to customer Stability of demand Time needed to add capacity Customer loyalty Ways to Decrease the Bargaining Power of Buyers Product differentiation Information available to buyers Customer interest in features vs. price Price as a percent of buyer’s income Switching costs for buyer Difficulty of copying product advantages Factors Influencing the Bargaining Power of Suppliers Five factors in the market for inputs Threat of new suppliers entering Bargaining power with regard to our suppliers Bargaining power of our suppliers Threat that we will switch to substitute inputs Rivalry among existing suppliers Threat of vertical integration Threat of Substitutes Examples include: Drive vs. fly Oil vs. gas heat Chicken vs. beef Home equity loan vs. auto loan The closer the substitutes, the more limited the power of the seller Rivalry Among Firms Goals of competitors Profit vs. size, for example Strength of competitors Cost advantage or disadvantage Financial strength Intelligence of competitors Creating Competitive Advantage on 3 Fronts Change or take advantage of some industry characteristics or market imperfection Create Create barriers to entry some form of product advantage Distribution Create advantage some form of cost advantage Pricing strategy Information management Using Strategy to Create Wealth Steps to strategic planning Establish goals Assess the environment -- opportunities and threats Assess the organization -- strengths and weaknesses Develop a strategy Develop operating processes that support the strategy -marketing, distribution, production, capital budgeting, financing Implement, monitor and control Evaluate and reward Summary Wealth creation is impossible in a perfect market Porter’s five forces can be used to evaluate the industries in which the firm operates or plans to to enter A strategy should be developed that allows the firm to utilize market imperfections to establish a sustainable competitive and consequently an economic profit or positive net present value Economic profit comes from competitive advantage in: Dealing with customers Dealing with financial markets