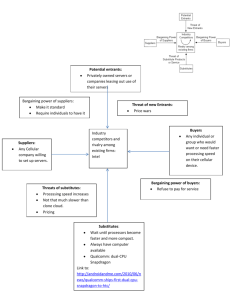
Management Tools & applications On completion of this session, you will be able to understand the usage and applications of the following management tools: • SWOT analysis • PESTEL analysis • Maslow hierarchy • Five Forces analysis • Stakeholder analysis • BCG matrix analysis The Management Tool – Porter’s five forces What is a Porter’s five forces analysis ? • a simple but powerful analytical tool for - understanding the competitiveness of your business environment - identifying strategy's potential profitability for your organization a renowned American academic well known for his theories on economics and business strategy an author of 18 books and numerous articles including Competitive Strategy, Competitive Advantage PHD in Harvard and the most cited author in business and economics Five Forces Analysis – Step by Step (1) Identify the different factors that bring about the competitive pressures for each of the five forces: - Is it difficult to enter this industry? - Who are the customers? - What are the substitute products? - Who are the suppliers? - Who are the major competitors in this industry? Five Forces Analysis – Step by Step (2) Based on the factors identified, determine if the pressures are: - Strong - Moderate - Weak Five Forces Analysis – Step by Step (3) Determine whether the strength of the five forces is favorable to earning attractive profits in the industry. Make use of the Five Forces model to answer the following questions: - Is the state of competition in the industry stronger than "normal"? - Can companies in this industry expect to earn decent profits in light of the competitive forces? - Are the competitive forces sufficiently powerful enough to undermine industry profitability? The threat of new entrants Refers to how easy or difficult for competitors to join the marketplace in the industry. The low barrier will bear greater risk for a business‘s market share being depleted. New entrants eventually will decrease profitability for other firms in the industry. Possible barriers to entry could include : • Economies of scale • Cost advantage of existing players • Brand loyalty The threat of new entrants Cont’d • Intellectual property like licenses • Access to raw materials is controlled by existing players • Existing players have secure customer relations • Legislation and government acts • etc…… Bargaining Power of Buyers refers to the power of the consumer to affect pricing and quality. • Consumers’ power is high / low when : - Customers procure large / small volume - the supplying industry consists of several / limited small operators - the supplying industry is controlled with high / low fixed costs - the product has / does not have substitutes - switching products is easy / difficult - Customers are price sensitive / not sensitive Threat of Substitutes When customers can have a lot of substitute for any products or services, buyers will determine the prices. On the contrary, when a business follows a product differentiation strategy, buyers cannot determine the prices. The threat of substitute is determined by : • Brand dependability of customers • Secure customer relationship Threat of Substitutes Cont’d • The relative price for performance of substitutes • Up-to-date trends • Switching costs for customers • Availability of close substitutes • Perceived level of product differentiation • etc…. Bargaining Power of Suppliers refers to the extent to which the suppliers can influence the prices. When there are a lot of suppliers, buyers can easily determine price in the industry. On the contrary, when the number of suppliers is relatively small, they can determine and push the prices up. The supplier bargaining power is high when: • the market is conquered by a few big suppliers • no alternative products available Bargaining Power of Suppliers cont’d • customer base is fragmented, making bargaining power low • high switching costs from one to another supplier • etc….. Rivalry Amongst Existing Competitors In highly competitive industries, firms can have no influence on the prices of the goods and services. In contrast, when the industry is a monopolistic competition or monopoly, businesses can fully control the prices of goods and services. Rivalry between existing players is likely to be high when : • • players are the same size players have comparable strategies Rivalry Amongst Existing Competitors Cont’d • little or no differentiation between players and their products • low market growth rate • barriers for exit are high • etc…….. Threats of new entrants Rivalry among existing competitors Threats of substitutes Five Forces Model Bargaining power of suppliers Bargaining power of buyers • Conduct a Five Forces Analysis on an industry suggested by your team • Please discuss amongst your group members (4 or 5 Students) on the above topic and participate the discussion 10 minutes later. Q/A