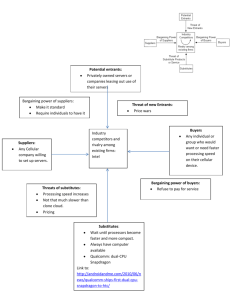
TOPIC 6: BUSINESS STRATEGY Strategic analysis and choice INTRODUCTION • Often, employees are concerned with the day-to-day running of a business. However, senior management often need to think about a range of issues to do with the business’s direction, its competitors, and so on. This is what we refer to here as strategic management. • the components of strategic management: 1. Strategic analysis 2. Strategic choice 3. Growth strategy • In this section, we will look at the first two, and then we’ll address the third in a subsequent topic. 1 STRATEGIC ANALYSIS Porter’s five forces model: • Put forward by Michael Porter back in the 1980s, this model was designed to get firms to consider the factors that might affect their competitiveness • These five forces are: 1. the bargaining power of suppliers 2. the bargaining power of buyers 3. the threat of potential new entrants 4. the threat of substitutes 5. the extent of competitive rivalry Porter’s Five Forces Model A lot of this relates back to what we’ve talked about in previous topics – competition, substitutes, and so on. Potential entrants Threat of new entrants Bargaining power of suppliers Suppliers Industry competitors Bargaining power of buyers Rivalry among existing firms Threat of substitutes Substitute products Buyers Ideally, a firm will be able to identify the main forces of competition it faces, however, sometimes this is easier said than done! Source: Michael E. Porter Competitive Strategy: Techniques for Analyzing Industries and Competitors, (The Free Press, 1980) 2 The value chain Value chain analysis • Developed by Michael Porter, designed to get firms to think about backwards and forward linkages of inputs and outputs the firm requires. • We can separate this into ‘primary activities’ and ‘support activities’. After-sales service Primary activities: • As the name suggests, this is concerned with all things to do with the production, distribution and sale of the product itself Marketing and sales Outbound logistics Secondary/support activities: • Whilst they don’t formally add value to the product itself, they ensure the primary activities are completed as efficiently as possible. Operations Inbound logistics STRATEGIC CHOICE Strategic choice focuses on choices that need to be made with respect to two aspects of the business – the external environment (the market), and the internal environment (within the firm itself) Environment or market-based choices • types of strategy a firm might adopt: • cost leadership • differentiation • Focus (a market niche) • importance of establishing: Resource-based strategy (internal) • defining and establishing core competencies (does the firm even have one?) • exploiting core competencies • conditions for core competencies • valuable • rare • the basis of a firm's competitive advantages • costly to imitate • the nature of the target market • non-substitutable 3 STRATEGIC CHOICE Reactions of competitors • As we’ve seen previously though, even after all that has been taken into consideration, strategic choice also often relies on strategic behaviour, and how the firm reacts to competitors (in other words – game theory!) 4