Intermediate Financial Management-5th ed.

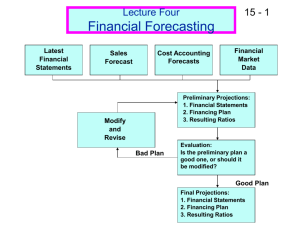
Financial Planning and Control
Financial Planning
Sales forecasts
AFN formula method
Financial plan
Set up a system of projected financial statements.
Determine the funds needed.
Forecast funds available.
Establish and maintain the system of controls.
Develop procedures for adjusting the basic plan.
Establish the performance-based
Financial Planning and
Control
Financial Planning
The projection of sales, income, and assets based on alternative production and marketing strategies, as well as the determination of the resources needed to achieve these projections.
Financial Control
The phase in which financial plans are implemented; control deals with the feedback and adjustment process required to ensure adherence to plans and modification of plans because of unforeseen changes.
Financial Planning:
The Sales Forecast
A forecast of a firm’s unit and dollar sales for some future period; generally based on recent sales trends plus forecasts of the economic prospects for the nation, region, industry, etc.
Sales Projection
(millions of dollars)
$3,000
$2,500
$2,000
$1,500
$1,000
$500
$0
2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014
Projected (Pro Forma)
Financial Statements
A method of forecasting financial requirements based on forecasted financial statements.
ADF = additional funds needed to support the level of forecasted operations
2011 Balance Sheet (in millions of $)
Cash & sec.
Accounts rec.
Inventories
Total CA
Net fixed assets
Total assets
$ 20 Accts. pay & accruals
240 Notes payable
240
$ 500 Total CL
L-T debt
Common stk
Retained
500 earnings
$1,000 Total claims
$ 100
100
$ 200
100
500
200
$1,000
2011 Income Statement
(in millions of $)
Sales
Less: Var. costs (60%)
Fixed costs
EBIT
Interest
EBT
Taxes (3 0%)
Net income
Dividends (30%)
Add’n to RE
$2,000.00
1,200.00
700.00
$ 100.00
16.00
$ 84.00
25 .20
$ 58.80
$ 17 .64
$ 41 .16
BEP
Profit Margin
ROE
DSO (days)
Inv. turnover
FA turnover
TA turnover
D/A ratio
TIE
Current ratio
Payout ratio
Key Ratios
NWC Industry Condition
10.00% 20.00%
2.52% 4.00%
7.20% 15.60%
43.2
32.0
8.33x
4.00x
2.00x
11.00x
5.00x
2.50x
30.00% 36.00%
6.25x
9.40x
2.50x
3.00x
30.00% 30.00%
Poor
Poor
Poor
Poor
Poor
Poor
Poor
Good
Poor
Poor
OK
Key Assumptions
Interest rate = 8% for any debt.
Operating at full capacity in 2011 .
Each type of asset grows proportionally with sales.
Payables and accruals grow proportionally with sales.
2011 profit margin (2.52%) and payout (30%) will be maintained.
Sales are expected to increase by
$500 million. (%
D
S = 25%)
Assets
1,250
1,000
Assets = 0.5 sales
D
Assets =
(A/S)
D
Sales
= 0.5(500)
= 250.
2,500
Sales
0 2,000
A/S = 1,000/2,000 = 0.5 = 1,250/2,500.
AFN formula
AFN= (A*/S)
D
S - (L*/S)
D
S - M(S
1
)(1 - d)
Additional funds needed
Required increase in assets
Spontaneous increase in liabilities
Increase in retained earnings
AFN formula
AFN= Additional funds needed
A*= assets that tied directly to sales, so must increase if sales are to increase
S = sales during the last year
D
S = change in sales =S
1
- S
L*= liabilities that increase spontaneously, normally include account payables and accruals, but not bank loans and bonds
M = profit margin = profit per $1 of sales
AFN formula
S
1= total sales projected for next year
(1 - d)= Retention ratio = the percentage of net income that retained
(A*/S) = percentage of required assets to sales, showing the required dollar increase in asset per $1 increase in sales
(L*/S) = liabilities that increase spontaneously as a percentage of sales, or spontaneously generated financing per $1 increase in sales
What is the AFN based on the AFN equation?
AFN = (A*/S)
D
S - (L*/S)
D
S - M(S
1
)(1 - d)
= ($1,000/$2,000)($500)
- ($100/$2,000)($500)
- 0.0252($2,500)(1 - 0.3)
= $250 - $25 - $44.1
= $180.9 million .
Questions the Financial Planner
Should Consider
Mark Twain once said
“ forecasting is very difficult, particularly if it concerns the future ”. The process of financial planning involves the use of mathematical models
Questions the Financial Planner
Should Consider
In assessing a financial forecast, the planner should ask the following questions:
Are the results generated by the model reasonable ?
Have I considered all possible outcomes?
How reasonable were the economic assumptions which were used to generate the forecast?
Which assumptions have the greatest impact on the outcome?