2. Modern financial markets I
advertisement

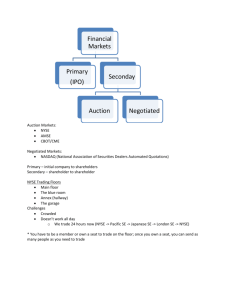
2. Modern financial markets 2.1 US equity markets The main US primary markets are the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and NASDAQ. What is primary market? There are also several US regional exchanges. Regional exchanges were created primarily to list local companies that could not afford to become listed in the national exchanges. Current regional exchanges include Boston, Chicago, Pacific, and Philadelphia exchanges. Boston and Philadelphia regional exchanges were acquired by NASDAQ in 2007. One of the primary markets, American Stock Exchange, was acquired by NYSE Euronext in 2008. In 2013, ICE bought NYSE Euronext. Two ECNs, BATS and Direct Edge, have become exchanges in 2008 and 2010, respectively. . 1 2. Modern financial markets 2.2 The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) The NYSE was founded as an open-outcry auction in the end of the 18th century and has evolved since then into a complex hybrid market combining an open outcry with a quote-driven (dealer) market and electronic LOB. For every stock traded on the floor, there is a designated dealer (specialist) who maintains the LOB and makes the market using his own account when there is lack of liquidity from other traders. Another specialist’s duty is conducting the opening and closing auctions. Specialists are not allowed to trade ahead of their customers at the same price on the same side of the market. In fact, trading by brokers and dealers for their own account using the knowledge of their customers’ pending orders (so-called front running) is illegal. 2 3 The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) 4 2. Modern financial markets 2.2 The NYSE (continued) In 2007, the NYSE introduced the Hybrid Market system. Traders now can directly submit their orders to the electronic LOB bypassing brokers and specialists unless their order size exceeds one million of shares. The reasons: - customers have more choices and faster execution - growing trading volume requires automatic execution - SEC has issued the new rule (Regulation NMS Order Protection Rule), which requires the market to honor better-priced quotes available in other “fast” markets before filling orders at the market’s own prices. Sub-second order execution is required for the status of “fast market”, which is accomplished by introduction of the Hybrid Market. 5 2. Modern financial markets 2.2 The NYSE (continued 2) Market orders and marketable limit orders in the Hybrid Market are by default executed automatically. There are however stock-specific price ranges (so-called Liquidity Replenishment Points) that determine the limits for price jumps and volatility. If these limits are reached, trading is converted from automatic to “auction only” execution. Introducing the Hybrid Market has reduced an average execution time from 10 seconds to less than one second. This, however, increased the bid/ask spread (i.e. cost of immediacy) by about 10% (Hendershott & Moulton (2010)). In 2007, the NYSE was merged with the pan-European electronic market Euronext into NYSE Euronext. November 2013, ICE completed takeover of NYSE. 6 2. Modern financial markets 2.3 NASDAQ NASDAQ was founded by National Association of Securities Dealers (NASD) in 1971. In 2007, NASD was consolidated with the member regulation, enforcement and arbitration functions of the NYSE into the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA), which is the largest independent regulator for all securities firms in the United States. NASDAQ is a purely electronic market: it does not have a physical floor, and its dealers and brokers are connected via electronic network. The specific of NASDAQ is that several competing dealers can trade stocks of the same company (rather than one specialist in the NYSE). 7 NASDAQ 8 2. Modern financial markets 2.4 Alternative trading systems (ATS) ATS are regulated by the SEC but are not registered as exchanges. Hence ATS cannot list new securities. ATS serve as alternative sources of liquidity and compete with exchanges for customers using lower execution latency and fees. There are two main types of ATS: electronic communication networks (ECN) and crossing networks (dark pools). 2.4.1 ECN ECN have electronic LOB and trading rules similar to those in continuous order-driven markets. They often permit only limit orders and offer possibility to trade before and after regular trading hours. Most ECN have been acquired or merged with exchanges, e.g. one of the first ECN, Instinet, was bought by NASDAQ in 2006 and ECN Archipelago was merged with the NYSE in 2006. BATS Exchange and Direct Edge were founded as ECN (in 2005 and 1998, respectively) but became exchanges in 2009 and 2010, respectively. 9 2. Modern financial markets 2.4 Alternative trading systems (continued) 2.4.2 Crossing networks (CS) There is no price discovery in CS where orders are matched upon prices quoted in the primary markets. Trading in CS has no explicit market impact. The first CS (ITG, Liquidnet, and Pipeline) offered anonymous block trading. Average trade sizes in these venues reach tens of thousands shares. Other CS have been implemented by several large brokers for internalization of their customers’ orders. In these CS, brokers can trade for their own account against their customers and typical order size is several hundred shares. These CS include Credit Suisse Crossfinder, Goldman Saks Sigma X, GETCO Execution Services, and Knight Link. In July 2013, GETCO and Knight completed merger. 10 2. Modern financial markets 2.5 European equity markets Major markets: London Stock Exchange and Deutsche Bourse. Markets in Financial Instruments Directive (MiFID) in 2007: - pre- and post-trade transparency (aggregated LOB, volumes) - best execution (across borders) Pan-European ATS (called in Europe the Multilateral Trading Facilities (MTF)): Chi-X (in 2009 volumes exceeded those of Madrid and Swiss stock exchanges), BATS Europe, Turquoise, several US ATS. 11 2. Modern financial markets 2.6 Global FX market 2.6.1 Introduction Most liquid market: ADV has grown from $3.3 trillion to $5.3 trillion between 2007 and 2013. Centers: London, New York, Tokyo; also: Singapore, Australia, Canada. Main currency pairs: EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD. Also: USD/AUD, USD/CAD, USD/CHF, EUR/JPY, EUR/GBP, EUR/CHF. Proxies to equities/commodities (?) pips Exchange rate (EUR/USD): 1.3456(5) decimal pip big figure 12 13 2. Modern financial markets 2.6 Global FX market (continued) 2.6.1 Introduction (continued) Difficult to estimate fair value… -Purchase power parity -Interest rates Why trade then? Import/export cash flows, hedging, speculation FX is OTC market: little international regulation 2.6.2 Spot FX Trading one currency for another with delivery usually taking place within two days after the dealing date (but USD/CAD – one day). The share of spot FX in the ADV in 2010 is estimated between 37% worldwide and 55% in the USA. 14 2. Modern financial markets 2.6.2 Spot FX (continued) Interdealer platforms: EBS (owned by ICAP) & Reuters-Thomson - Limit orders only Credit screening Prime bank business model Distributed architecture (EBS) Dealer-to-client platforms - multi-dealer platforms (Currenex, HotSpot, FXall) - bank portals (Citi, Deutsche) - retail brokerages (FXCM, Gain) 15 2. Modern financial markets 2.6.3 Other FX instruments (Dodd-Frank -> SEF) FX swap is a contract that simultaneously agrees to buy (sell) an amount of currency at agreed rate and to resell (repurchase) the same amount of currency for a later date to (from) the same counterparty, also at agreed rates (44% worldwide and 31% in USA) . Outright forward is a contract to exchange a predetermined amount of one currency for another at an agreed date in the future, based upon a rate of exchange determined at the trade date of the contract (~13%). FX option is a contract that gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to exchange one currency for another at a predetermined exchange rate on or until the maturity date. NDF is similar to outright forward but there is no physical settlement of two currencies at maturity. Rather, based on the movement of two currencies, a net cash settlement will be made by one party to the other – usually in US dollars. In currency swap, interest and principal in one currency are exchanged for interest and principal in another currency. 16 2. Modern financial markets 2.7 US fixed income market Instruments: UST, money market, ABS, MBS, agencies (Fannie Mae), municipal bonds. Interdealer brokers: Brokertec (owned by ICAP), eSpeed (owned by the BGC Partners), and Tradeweb (owned by several financial institutions with Reuters-Thomson having a majority stake). “Workup” (expandable limit order) 27 Price in 90.27 (90-27) = 90 32 27 1 Price in 256th: 90.27+ = 90 + 32 64 32nd: 27 3 90.273 = 90 + 32 256 17 2. Modern financial markets 2.7 High-frequency trading (HFT) Portfolio turnover from seconds to hours HFT => technology (microwave?) + co-location Leveling the field: IEX’s “speed bump”, MQL, randomization of LOB 2.7.1 HFT strategies: - market making (rebates) - statistical arbitrage - event/news arbitrage - slicing large orders (algorithmic trading) 18 2. Modern financial markets 2.7 High-frequency trading (continued) 2.7.2 HFT controversies - unregulated liquidity source (flash crash of 2010) high volume != high liquidity (“hot potato” effect) circuit breakers (10% price fall within 5 min => 5-min pause) Toxic trading: - sponsored (naked) market access (banned in Nov 2010) - stub quotes (banned; deviation from national best less than 8%) - quote stuffing (submitting lots of orders) - quote spoofing/layering (submitting orders for provoking price change) -pump and dump (pushing price of illiquid instrument by small orders) -pooling (two traders trade among themselves at artificial prices) 19 Materials about HFT • http://tabbforum.com/opinions/hft-in-search-of-thetruth?page=3&utm_campaign=36d190f832-UA-121603921&utm_medium=email&utm_source=TabbFORUM+Alerts&utm_term=0_29f4b8f8f136d190f832-272896141 • https://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_embedded&v=ItfAKguEdAE#at=63 • http://www.birs.ca/events/2013/5-day-workshops/13w5008/videos • http://www.amazon.com/Problem-HFT-Collected-FrequencyStructure/dp/1481978357/ref=sr_1_1?s=books&ie=UTF8&qid=1384719035&sr=11&keywords=bodek • http://www.amazon.com/Flash-Boys-MichaelLewis/dp/0393244660/ref=sr_1_1?s=books&ie=UTF8&qid=1419256380&sr=11&keywords=flash+boys • http://www.amazon.com/Flash-Boys-Insiders-Perspective-HighFrequency/dp/0692336907/ref=tmm_pap_title_0#customerReviews 20