Cost Accounting
advertisement

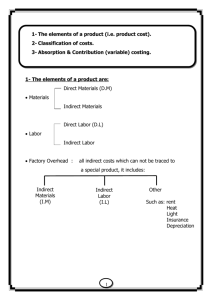
Cost Accounting Introduction of cost accounting Lecture-1 By Main Ahmad Farhan (ACA) Accounting It is a language about financial information (which is measurable in terms of money) commonly used in business. Branches Of Accounting Accounting Financial Accounting For external reporting Cost Accounting Management Accounting For internal reporting Fed by financial and cost accounting User Group User Group Financial Accounting Cost & Management Accounting Investors Managers Lenders Directors Govt Agencies Suppliers Management Employees Branches Of Accounting Financial Accounting is an art of recording (Journal), classifying (Ledger), summarizing (Trial balance), reporting (Profit & Loss A/c & Balance Sheet) and analysis (Interpretation) the financial information. Cost Accounting deals with ascertainment, measurement, accumulation, budgeting and evaluating cost structure of the entity. Management Accounting deals with decisions relating to the generation and effective utilization of the financial resources of an entity. Cost Accounting So Cost accounting is a specialized branch of accounting which provide processed set of information / statements to the management which assist them in decision making. In cost accounting cost of product or a process is; Ascertained Measured Accumulated Management Accounting Management is central coordinating body in an entity Management is concerned with the maximization of wealth through Minimization of cost Maximization of profit For this purpose information provided by cost accounting is analyzed by the management for decision making and management control function. Management Accounting Reports generated through management accounting are used internally. Major function of management accounting: • Planning & Forecasting • Controlling • Decision making Pricing Make or Buy Shut down or Continued operation Equipment Replacement Purpose Of Cost Accounting Provides information relating to cost of production. Determines the appropriate selling price. Discloses profitable products, areas and activity level. Helps in make or buy decision. Budgeting relating to production function. Controls production variances. Provides information to financial accountant. Classification Of Cost Cost Classification Direct Cost Direct Material Direct Labor Indirect Cost Other Direct Expenses Factory Overhead Direct Cost Cost that can be traced in full to the product or services is direct cost Types Of Direct Cost Direct material costs are those cost of material that are traceable in full in the cost of a product or services For example wood in manufacturing of table Direct labor cost is specific cost of the worker in producing a product or service For example labor involved in cutting wood Types Of Direct Cost Other Direct Expenses These are expenses other than direct material and direct labor which have been incurred in full as direct consequences of producing product or services Royalty on production, Cost of jigs / moulds Indirect Cost The cost that is incurred in producing product or services but which can not be traced in full Factory overhead (FOH) FOH means all expenses of factory other than direct material, direct labor and other direct production expenses. Indirect material Indirect Labor Deprecation of machinery Factory utility bills Cost classification Direct Material + Direct Labor + Other Direct Cost = Prime cost Direct Labor + Other Direct Cost + FOH = Conversion cost Prime Cost + FOH = Total factory cost Summary Material cost Labor cost Other production Total production cost Direct Direct Indirect Indirect Total Total cost Direct = Prime cost Indirect = FOH cost Total = Total Factory Cost Cost classification Direct material Direct labor Other direct cost Prime cost FOH Indirect material Indirect labor Electricity bill Rent of factory Depreciation Total factory cost Rs 12,000 8,000 2000 22,000 3000 2000 1500 3500 1000 11000 33000 Behavior Of Cost Fixed cost Variable cost Step fixed cost Semi variable cost Fixed cost Fixed cost is a cost that do not vary with the level of production. Simple means the variation in production has no impact on fixed cost. For example rent of building and accountant salary etc 3000 Fixed cost 2000 1000 100 200 No. of units 300 Fixed Cost Per Unit Reaction Fixed cost per unit decreases as the number of units produced increases and vice versa For example rent of building is Rs. 10,000 and number of units produced is 5000. Per unit fixed cost = 10000 / 5000 = 2 per unit If the number of units produced increases to 10000 Per unit fixed cost = 10000 / 10000 = 1 per unit Step Fixed Cost Costs which are constant for a relevant range of activity and rise to new constant level once that range exceeded. For example rent. Fixed cost No. of units Variable Cost The expenses that vary in direct proportion to volume of product. For example Prime cost. Variable cost No. of units Variable Cost Per Unit Reaction Variable cost per unit remain constant Units of Labor Total wages Per labor wage rate 10 10,000 1,000 20 20,000 1,000 Semi Variable Cost The cost that is partly fixed and partly variable cost. For example electricity bills, salesman salary. 3000 Semi variable cost 2000 1000 100 200 No. of units 300 Summary If the production volume increases Per unit Fixed cost Variable cost Total cost Total Decreases Constant Constant Increases Decreases Increases Summary If the production volume decreases Per unit Fixed cost Variable cost Total cost Total Increases Constant Constant Decreases Increases Decreases Total cost Total cost include both fixed cost and variable cost As VC added in FC shifts upward Total cost Variable cost 3000 Total cost 2000 Fixed cost 1000 100 200 No. of units 300