Manufacturing Costs - University of North Florida

Chapter 29
Managerial Accounting
Manufacturing Costs
Prepared by Diane Tanner
University of North Florida
Manufacturing vs. Merchandising
Operations
Merchandising Companies Manufacturing Companies
• Buy products
• Sell products
• Buy materials
• Use labor and other economic resources to produce products
• Sell products
2
3
Manufacturing vs. Merchandising
Inventories
Merchandising Companies Manufacturing Companies
Balance Sheet Balance Sheet
Current Assets
Inventories ….$4,000
3 separate inventories
Current Assets
Raw Materials ……..$4,000
Work in Process …....1,000
Finished Goods …….1,200
Both Merchandising & Manufacturing Companies
Income Statement
Sales ……………………………$34,000
Less cost of goods sold ……...21,000
Manufacturing or Non-manufacturing?
The Key Think about where in the operational process the cost occurs.
If the cost occurs in the factory while being produced
If the cost occurs after the product is produced or outside the factory
4
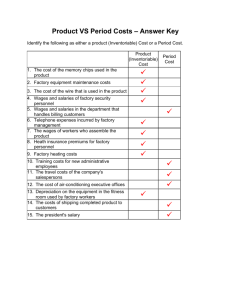
Product Costs
Expensed when the product is sold
Period Costs
Expensed in a period unrelated to sales
Product Costs for Manufacturers
Direct Materials
• Traced to products
• Easily identified with specific products
Direct Labor
• Traced to products
• Easily identified with specific products
5
Manufacturing
Overhead
• Allocated to products
• Not easily identified with specific products
Only product costs (not period costs) are labeled as direct or indirect.
6
Direct Material Costs
Material costs that can be traced to products or services provided
Includes all materials costs directly related to getting the materials ready to use (ultimately to get the product ready to sell)
Invoice cost to buy materials
Less cash discount
Plus sales taxes
Plus freight-in
Parallels accounting for merchandise inventory
7
Direct Labor
Labor costs that can be directly traced to products or services provided
Includes all direct labor needed to get the product ready to sell
Assumed to be hourly wages
Fringe benefits should be included as part of the hourly rate
8
Manufacturing Overhead
INDIRECT manufacturing (product) costs that cannot be traced directly to specific units produced, but are costs of production
Indirect materials
• Factory supplies
• Oil, lubricants, blades
• Glue, staples
Indirect labor
Factory-related costs
• Janitor labor
• Production supervisor labor
• Dedicated cost accountant labor
• Factory and equipment depreciation
• Factory insurance
• Factory rent and utilities
• Other factory costs
9
Product Cost Examples
Direct
Materials
Examples:
Lid, bottle, label, water
Manufacturing
Overhead
Direct
Labor
Examples:
Wages and fringes for assembly and packaging
The Product
Examples:
Factory supervisor and factory janitor salaries (indirect labor), indirect materials (supplies), factory rent/ insurance/depreciation/ utilities
10
Period Costs
Known as ‘Operating Expenses’
Not associated with the production of goods
Examples:
Selling, advertising, marketing costs, delivery costs
General and administrative ‘corporate’ costs
Corporate rent, insurance, utilities, depreciation
R&D costs, product development costs, accounting and payroll department costs, President Delaney’s salary
11