File
advertisement

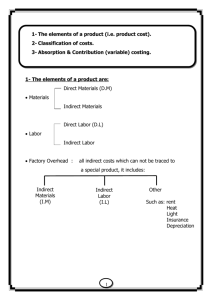
Chapter No.02 COSTS , CONCEPTS, USES AND CLASSIFICATIONS McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2006, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. “COST” IN COST ACCOUNTING Cost:The American Accounting Association Committee on Cost concept and standards define cost: Cost as “forgoing measured in monetary terms, incurred or potentially to be incurred to achieve a specific objective. KARDAN INSTITUTE OF HIGHER EDUCATION DISTINCTION BETWEEN COST AND EXPENSE Cost: Cost represents the amount invested in obtaining a product or service which has not yet expired, or benefits or services of which have not yet be received or which have not yet been utilized or consumed in connection with the realization of revenue. Prepaid expense, inventories of various kinds, properties and other asset, represents examples of Cost. Expense: Expenses refers to that cost which has expired or which has been charged against revenue of a period. E.g. cost of goods sold, salaries expenses etc. 3 Classification of cost:There are various way of classifying costs. Each classification serves a different purpose. Important classifications are given below: Functional Classification:1 - Manufacturing cost or production cost These are the costs which are incurred to produce items. Eg. Direct materials, direct labour and factory overhead. 2 - Commercial Expenses Distribution and selling Expenses: These are the Administration Expenses: These KARDAN INSTITUTE OF HIGHER EDUCATION expenses which are incurred to sell and distribute the products to customers .e.g. advertising expenses, transport expenses, delivery expenses etc. are the expenses which are incurred to manage and supervise the overall activities of an organization. e.g. office stationery, accounts department expenses, office transport and delivery etc. 4 Cost with the Respect to Product or Period:- 1 – Product Costs = These are the costs which are incurred or paid with respect to produce an item.e. g. Direct Materials, Direct Labour and Factory overhead. 2 - Period Costs = These are the costs which are incurred with respect to period.e.g. Salaries, rent, telephone bills and electricity bills etc. KARDAN INSTITUTE OF HIGHER EDUCATION 5 Direct Costs and Indirect Costs Material There are Two types of Materials. 1 - Direct Material: All that materials which can be directly identified with the cost of a product. Examples:Timber in chair or table, cloth in shirt. Basic or essential packing material like cartons, boxes, papers etc. KARDAN INSTITUTE OF HIGHER EDUCATION 2 - Indirect Material: Material cost which can not be allocated or identified but which are to be absorbed by the units produced. Example:Fuel, lubricants, tools for general use, glue, thread in shirts, nails in shoes etc. 6 Labour There are Two types of Labour. Direct Labour:All that labours which can be directly identified with the cost of product. All labours expending in converting raw material into desirable goods. KARDAN INSTITUTE OF HIGHER EDUCATION Indirect Labour:Labour cost which can not be directly allocated or identified, but which are to be absorbed by the units produced. Example: idle time wages, maintenance and repair, wages leave pay employers contribution to fun. 7 Factory overhead( FOH): - The aggregate of indirect material cost, indirect wages and indirect expenses.” Component Of Factory Overhead Factory Overhead = KARDAN INSTITUTE OF HIGHER EDUCATION Indirect Material + Indirect Labor + Others Indirect Cost 8 Component Of Factory Overhead Other Indirect Cost Indirect Material Factory Supplies Lubricants and fuel Indirect Labor Supervision (factory supervisor KARDAN INSTITUTE OF HIGHER EDUCATION salaries) Superintendence (Salary) Inspection team Salary Salaries of factory clerks Rent Insurance Fire Depreciation of Plant and machinery Maintenance and Repairs (Factory machinery, factory Building) Power (factory) Heat and Light of Factory Miscellaneous Factory overhead 9 By combining the foregoing elements of cost, the following divisions can be secured: 1. Prime Cost: This is generally used to denote the sum of direct material and direct labor cost. 2. KARDAN INSTITUTE OF HIGHER EDUCATION Conversion Cost: This term is generally applied to the sum of direct labor and factory overhead cost. In other words these are the costs which are incurred to convert raw materials into finished goods 10 Costs in their Tendency vary with volume or Activity KARDAN INSTITUTE OF HIGHER EDUCATION Fixed Costs:It refers to those expenses which do not vary with increase or decrease in production level. Total amount of fixed overhead remains constant –with all level of production. Fixed cost per unit change with increase or decrease of production level. Example:Factory building rent, salary of plant manager, insurance premium, depreciation etc. Variable Costs:It refers to those expenses which vary with the increase or decrease in production level. Total amount of variable overhead changes with all level of production. Variable cost per unit fixed with increase or decrease of production level. Example:direct materials, direct labour, Power, overtime, maintenance cost etc. 11 Semi – variable costs The few part of cost is fixed and few is variable costs. Example: Telephone expenses consist of rent charges and call charges. Rent charges are fixed while call charges is variable. Total of rent and call charges become semi – variable cost. KARDAN INSTITUTE OF HIGHER EDUCATION 12 USES OF COST DATA Planning profits by means of budgets. Controlling costs via responsibility accounting system. Measuring annual or periodic profit including inventory costing. Assisting in establishing selling prices and a pricing policy. Furnishing relevant cost data for analytical process for decision making. COST WITH RESPECT TO DEPARTMENTS Departmental costs: Which can be directly attributable to each department specifically.e.g. indirect materials, indirect labour etc. Common costs: Which can not be directly attributable to specific department.e.g. factory rent, insurance, canteen costs, repair and maintenance and factory depreciation JOINT COSTS These costs occur when the production of one product may be possible only if one or more other products are manufactured at the same time.e.g costs in meat industry packing industry, oil and gas industry etc. COSTS FOR PLANNING AND CONTROL Budgeted costs: Costs estimated for a specific period are called budgeted costs. These costs are used for planning and control purpose. Standard costs: It is the estimated cost per unit of an item. On the basis of standard costs the budget can be prepared. With the help of standards the variances can be calculated and responsibilities are identified. EXERCISES 01 Classify the following costs as to fixed, variable or semi variable. Explain the reasons for your classification of the semi variable costs. Depreciation- straight line method Rent Direct materials Repairs to machinery Factory insurance FICA tax Heat, light and power Superintendence Indirect labor Washroom supplies EXERCISES 02 Under which subheading of the elements of cost should each of the following costs be classified Cutting tools Inspector ‘s salary Depreciation of factory Legal expenses Earnings of mechanist Lubricating oil Supervisor ‘s wages Salary of factory store clerk Maintenance parts for factory equipment wages of factory crane operator EXERCISES 03 Classify the following items as direct or indirect materials: Ailerons on an airplane Seats to be installed in a railway car 1-oz, perfume bottle Stainless steel cone that holds the mirror in a color television set Sanding Material in furniture making Bags in flour mills Milk to make ice cream Ingots used by a foundry for making castings EXERCISES 04 Bid calculations. The Shepard Company is to submit a bid on the production of 10,000 ceramic salad bowls. It is estimated that the cost of materials will be $7,500 and direct labor, $ 10,100. Factory overhead is applied at $5 per direct labor hour in the Molding Department and at 120% of the direct labor cost in the finishing Department. It is estimated that 800 direct labor hours will be required in Molding and the direct labor cost in Finishing will be $ 4,300. The company wishes a bid price consisting of a markup of 40% of its total production costs. Required: Estimated cost to produce Estimated prime cost Estimated conversion cost Bid price