Accrued Expenses - Accounting = FuN
advertisement

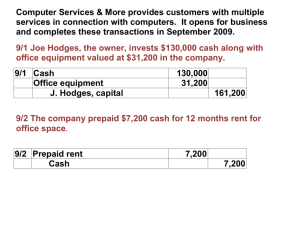
1 Your mobile phone bill shows that you have not settled last month’s amount. This month mobile phone bill shows an outstanding amount of $100 and the current amount of $80. Hence this outstanding amount of $100 is also known as accrued expense. 2 Balance Day Adjustments - Accrued Expenses – Phua CK is pretending to be calm but actually is very confused. He 1 should have paid Scenario $12 000 for the rent for the period from January to December 2000. – However, at the end of the period, he only paid $5 000 to Tan Ah Teck Pte Ltd due to negligence. He still owes the company $7 000. He does not know the correct entries to reflect this! Let us help him. End of accounting period – December 2000 – Should have paid : $ 12 000 – Paid only : $ 5 000 – Owed : $ 7 000 This owing amount of $7 000 is also known as Accrued Rent Expense. Mr. Phua CK still owes Tan Ah Teck Ltd $7 000 that was not paid for the year of 2000. Balance Day Adjustments - Accrued Expenses Definition: • Are expense that have been incurred for the accounting period BUT amount not yet paid for by the business. Balance Day Adjustments - Accrued Expenses What isCredit the Yes…. nature of entry because accrued it is a liability expense? (still owe Debit or Credit people $) entry? Using Phua CK as an example. If Mr. Phua remembered to pay the rent amount in full, then the entries will be:JOURNAL Date Particulars Year 2000 Dec 31 Rent Expense Profit and Loss a/c Debit Credit $12 000 However, this is not the case. An additional ledger needs to be created – Accrued Rent Expense $12 000 JOURNAL Date Particulars Year 2000 Debit Rent Expense $7 000 Rent Expense (Accrued) Dec 31 Credit $7 000 RENT EXPENSES a/c Year 2000 Dec 31 Bank Bal c/d $5 000 Year 2000 Dec 31 Profit & Loss $12 000 $7 000 $12 000 $12 000 Year 2001 Jan 1 Bal b/d $7 000 JOURNAL Date 2000 Dec 31 Particulars Profit & Loss a/c Debit Credit $12 000 Rent Expense $12 000 (Being rent expense closing off to P&L a/c) Profit & Loss Account 2000 Dec 31 Expenses $12 000 Balance Sheet as at Dec 2000 Liability Accrued Rent Expense $7 000 Balance Day Adjustments - Accrued Expenses Summary • Definition • Credit/Debit nature? • Is there a need to open another ledger for accrued expense? • Post this ledger to P/L or Balance Sheet? 11 Your father is very angry! Due to Economic crisis, the company your father is working for is unable to pay him salary for this month. However, his salary will be delayed till next month. • Assume that your father is earning a monthly salary of $5 000. The company will pay in total of $10 000 to your father next month ($5 000 x 2), being one month of salary owing to your father. This owing salary is known as ACCRUED Salary. This applies same to firms whereby revenues owing to them is known as Accrued Revenues. Definition Are revenues earned for the current accounting period but not yet received as cash payment. 13 Accrued Revenue/Outstanding Revenue •Scenario Mr Tan sub-lets 1 a building for Phua CK for a monthly rental of $1 000. Due to Phua’s negligence, Mr Tan does not receive $12 000 for period from January to December 2000. Instead Mr Tan only receives $5 000 from Phua. 14 Accrued Revenue/Outstanding Revenue End of accounting period – December 2000 – Should have received : $ 12 000 – Only received : $ 5 000 – Outstanding revenue : $ 7 000 This owing amount of $7 000 is also known as Accrued Rent Revenue. Mr. Tan still owes PCK Ltd $7 000 that was not paid for the year of 2000. 15 Accrued Revenue/Outstanding Revenue 1 Jan 2000 31 May 2000 $ 5 000 received 31 Dec 2000 $7 000 owing $12 000 earned JOURNAL Date Year 2000 Dec 31 Particulars Rent Revenue (Accrued) Rent Revenue Debit Credit $7 000 $7 000 16 Accrued Revenue/Outstanding Revenue RENT REVENUE a/c Year 2000 Year 2000 Dec 31 Profit & Loss $12 000 Dec 31 Bank 31 Year 2001 Jan 1 Bal b/d Bal c/d $12 000 $5 000 $7 000 $12 000 $7 000 PROFIT AND LOSS a/c Year 2000 Dec 31 Rent $12 000 Revenue 17 RENT REVENUE a/c Year 2000 Year 2000 Dec 31 Profit & Loss $12 000 Dec 31 Bank 31 Year 2001 Jan 1 Bal b/d Bal c/d $12 000 $5 000 $7 000 $12 000 $7 000 BALANCE SHEET AS AT 31 DEC 2000 Current Asset Accrued Revenue $7 000 18 Balance Day Adjustments - Accrued Revenue • Definition • Nature of the entry - Debit or Credit entry? • Distinguish the differences in adjustments between the Accrued Expenses and Accrued Revenues 19 20 Singtel has a promotion for new subscribers. If you paid the 6 months of mobile-phone monthly subscription upfront NOW, you get a free Nokia 8250. Assuming that the monthly subscription is $20. You like the promotion and paid $1 200 (6x$20) immediately in order to get the new mobile phone. Hence you are paying in advance for the expense. The payment in advance of subscription fees ($1 200) is also known as Prepaid Expense. Prepaid Expense/Payment in Advance Definition Are expenses that have been paid in advance but NOT yet incurred for the current accounting period. Since expense Prepaid isexpense a debit is entry. the like anIfasset expense hadas to the firm been prepaid, it is similar to what will be people owing the naturetoof services the theentry? firm. Hence a DEBIT ENTRY. Prepaid Expense/Payment in Advance Scenario 2 Phua CK learnt his lesson last time of not paying on time last year, so he decides to pay in advance to “save his face” this year. The rent expense for the accounting year of 2001 is $12 000, but he pays $18 000. Hence he prepaid $6 000 for expenses that has not been incurred in 2001. Prepaid Expense/Payment in Advance Recall that the monthly rent expense is $1 000. Hence from January to December 2001, the total rent is $12 000. Phua CK prepaid rent expense of $6 000 for January to June 2002. 1 Jan 2001 31 Dec 2001 30 June 2002 $ 12 000 incurred $18 000 paid $6 000 prepaid JOURNAL Date Year 2001 Particulars Rent Expense (Prepaid) Dec 31 Debit Credit $6 000 Rent Expense $6 000 RENT EXPENSES a/c Year 2001 Dec 31 Bank Year 2001 $18 000 Dec 31 Balance c/d Profit & Loss $18 000 Year 2002 Jan 1 Bal b/d $6 000 $ 6 000 $12 000 $18 000 Profit & Loss Account 2001 Dec 31 Expenses $12 000 Balance Sheet as at Dec 2001 Current Assets Prepaid Rent Expense $6 000 Summary • Definition • Credit/Debit nature? • What are the differences in adjustments between the accrued and prepaid expenses? 29 Balance Day Adjustments You have found a part-time job in MacDonald for three months. Your monthly salary is $500. By the end of the first month, you should have received $500 of what you have earned. However, the manager is such a nice person that he gives you $1 000. (Two months’ salary). He understands that you need money to enjoy your school holidays. 30 Balance Day Adjustments Received : $500 x 2 (Two month’s salary) = $1 000 Earned : $500 Paid in advance : $500 This prepaid of salary (revenue) is known as Prepaid Revenue / Outstanding Revenue. $500 is the prepaid Revenue. 31 Prepaid Revenue/ Outstanding Revenue DEFINITION Are revenues received in advance for which the services not yet rendered/earned in the particular accounting year. Hence the received cash for such revenues is not considered as revenues for the current accounting year. 32 Prepaid Revenue/ Outstanding Revenue Scenario • Recall that Mr2 Phua CK decided to pay in advance his rents to “save face”. Hence Mr Tan received $18 000, in which $12 000 is the revenue earned for the accounting year of 2001 and $6 000 is prepaid revenue. 33 Prepaid Revenue/ Outstanding Revenue 1 Jan 2001 31 Dec 2001 $ 12 000 earned 31 June 2002 $6 000 in advance $18 000 received JOURNAL Date Credit Year 2001 Dec 31 Particulars Prepaid Rent Expense Rent Expense Debit $6 000 $6 000 34 Prepaid Revenue/ Outstanding Revenue RENT REVENUE a/c Year 2001 Year 2001 Dec 31 Profit & Loss $12 000 Dec 31 Bank Prepaid rent Revenue $18 000 $6 000 $18 000 $18 000 PROFIT AND LOSS a/c Year 2001 Dec 31 Rent $12 000 Revenue 35 Prepaid Revenue/ Outstanding Revenue PREPAID RENT REVENUE a/c Year 2001 Dec 31 Bal c/d Year 2002 Jan 1 Bal b/d Year 2001 $6 000 Dec 31 Rent Revenue $6 000 $6 000 $6 000 $6 000 BALANCE SHEET AS AT 31 DEC 2001 Current Liabilities Prepaid Revenue $6 000 36 Balance Day Adjustments - Prepaid Revenue • Definition • Nature of the entry • Distinguish the differences in adjustments between accrued revenues and prepaid revenues 37 38 Practice - Accrued and Prepaid Revenues Trial Balance as at 31 August 2001 Particulars Rent Commission Debit $ Credit $ 1 500 7 000 Adjustments 1) $300 of the rent revenue was received in advance. 2) The monthly commission was $700. The accounting period is from 1 July 2000 to 31 August 2001 39 Practice - Accrued and Prepaid Revenues Particulars 1 JOURNAL Rent Revenue Debit Credit $ $ 300 Prepaid Rent Revenue 300 (Being amount of revenue received in advance) 2 Accrued Commission Revenue Commission Revenue 1 400 1 400 (Being revenue earned but not yet received) 40 Prepaid Rent Revenue 1 Rent Revenue Prepaid Rent Rev Profit & Loss $ 300 Cash at Bank 1 200 $ 1 500 Prepaid Rent Revenue $ Bal c/d 300 $ Rent Revenue 300 Profit & Loss for the year ended 31 Aug 2001 $ Rent Revenue $ 1 200 Balance Sheet as at 31 Aug 2001 $ Current Liability Prepaid Rent Rev $ 41 300 2 Accrued Commission Revenue Commission Revenue $ Profit & Loss $ 8 400 Cash at Bank Accrued Comm Rev 7 000 1 400 Accrued Commission Revenue $ Rent Revenue $ 1 400 Bal c/d 1 400 Profit & Loss for the year ended 31 Aug 2001 $ Rent Revenue $ 8 400 Balance Sheet as at 31 Aug 2001 Current Asset Accrued Comm Rev $ 1 400 $ 42 Conclusion Accrued Expenses Amount incurred for the accounting period but not yet paid for. Credit Entry Prepaid Expenses Amount not yet incurred for the accounting period buy have been paid for. Debit Entry Accrued Revenues Amount earned for the accounting period but not yet received as cash payment. Debit Entry Amount not earned for the accounting period but have been paid for. Credit Entry Prepaid Revenues 43 Conclusion Accrued Expenses Prepaid Expenses Accrued Revenues Prepaid Revenues Dr Expense A/C Cr Accrued Expense A/C Dr Prepaid Expense A/C Cr Expense A/C Dr Accrued Revenue A/C Cr Revenue A/C Dr Revenue A/C Cr Prepaid Revenue A/C 44 Conclusion Accrued Expenses Current Liability Prepaid Expenses Current Assets Accrued Revenues Current Assets Prepaid Revenues Current Liability 45 46 Practice - Accrued and Prepaid Expenses • During the year of 2001, the cash book shows: • maintenance Expense • Selling Expense $ 900 $1 200 • On 31 May 2001, the Balance Sheet also shows • Prepaid Maintenance Expense • Accrued Selling expense $ 400 $ 300 • Find the actual amount of the expenses incurred for the year of 2001. 47 1 Prepaid Maintenance Expense Maintenance Expense $ Cash at Bank 900 $ Profit & Loss 500 Prepaid Maint Exp 400 900 2 900 Accrued Selling Expense Selling Expense $ Cash at Bank Accrued Selling Exp 1 200 Profit & Loss $ 1 500 300 1 500 1 500 48 • Page 148 49