Adjusting Entries
advertisement

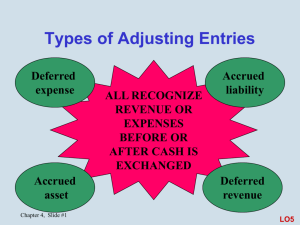
Adjusting Entries Measuring Business Income Accounting period assumption Cash accounting versus accrual accounting Matching principle Materiality concept Adjusting Entries Journal entries that update the general ledger accounts to state revenues, expenses, assets, and liabilities more accurately Involve – One balance sheet account – One income statement account – Never cash Adjusting Process Identify the accounts requiring adjustment Determine unadjusted balances Determine correct (adjusted) balances for each account Prepare adjusting entry to bring accounts in agreement with adjusted balances Deferrals A cash payment or receipt occurred in current period Must defer a portion of expense or revenue until a future period Deferrals Two situations – Pay a cost of benefit in advance and allocate cost as expenses to periods that receive benefit Deferrals Two situations – Pay a cost of benefit in advance and allocate cost as expenses to periods that receive benefit – Receive a cash revenue in advance and allocate amounts as revenues to periods in which revenues earned Prepaid Insurance Dec. 1, paid $600 for 12 month insurance premium recording as asset, Prepaid Insurance At Dec. 31 – Prepaid Insurance balance $600 – Insurance Expense balance $0 Prepaid Insurance As of Dec. 31, one month’s insurance has expired and become expense Correct Dec. 31 balance – Prepaid Insurance $550 – Insurance Expense $50 Prepaid Insurance Adjusting entry – Debit Insurance Expense $50 »Increases Insurance Expense to correct balance $50 – Credit Prepaid Insurance $50 »Decreases Prepaid Insurance to correct balance $550 Depreciation Expense Similar to prepaid insurance but for long-term asset Decrease in asset not recorded in asset account Recorded as increase in contra asset - Accumulated Depreciation Depreciation Expense Before Balance Sheet $26,000 Trucks 400 Accum Deprec After $26,000 800 Income Statement Depreciation expense $0 $400 Unearned Revenues Dec. 1, received $600 for 6 month rent recording as liability, Unearned Rent At Dec. 31 – Unearned Rent balance $600 – Rent Revenue balance $0 Unearned Revenues As of Dec. 31, one month’s rent has been earned and become revenue Correct Dec. 31 balance – Unearned Revenue $500 – Rent Revenue $100 Unearned Revenues Adjusting entry – Debit Unearned Rent $100 »Decreases Unearned Rent to correct balance $500 – Credit Rent Revenue $100 »Increases Rent Revenue to correct balance $100 Accruals Recognize revenues and expenses that have accumulated (accrued) during the accounting period but have not been recorded Accrued Revenues Dec.11, received 30-day, 15% note from customer. At Dec. 31 – Interest Revenue balance $0 – Interest Receivable balance $0 Accrued Revenues As of Dec. 31, 20 days interest has been earned and become revenue $1,200 x 0.15 x 20/360 = $10 Correct Dec. 31 balance – Interest Revenue $10 – Interest Receivable $10 Accrued Revenues Adjusting entry – Debit Interest Receivable $10 »Increases Interest Receivable to correct balance $10 – Credit Interest Revenue $10 »Increases Interest Revenue to correct balance $10 Accrued Expenses Employees paid Friday for 5-day work week at $1,000 per week At Dec. 31, a Tuesday – Wages Expense balance $50,000 represents past weeks wages – Wages Payable balance $0 Accrued Expenses As of Dec. 31, 2 days wages have been incurred and become expense Correct Dec. 31 balance – Wages Expense $50,200 – Wages Payable $200 Accrued Expenses Adjusting entry – Debit Wages Expense $200 »Increases Wages Expense to correct balance $50,200 – Credit Wages Payable $200 »Increases Wages Payable to correct balance $200 Summarize Adjustments Analyzing Information Use questions to compare companies Income Statement Which company has the higher revenues? Which company has the higher percentage change in revenues? Which company has the lower percentage of expenses to revenues? Balance Sheet Which company has the higher assets? What is the percentage change in assets for each company? Is the percent of total liabilities to total liabilities plus owners’ equity increasing or decreasing? Which company is more risky? Integrative Analysis Are companies operating efficiently by using least amount of assets to generate a given level of revenues? – Calculate total asset turnover Are companies operating efficiently by using least amount of assets to generate a given net income? – Calculate return on assets