Document
advertisement
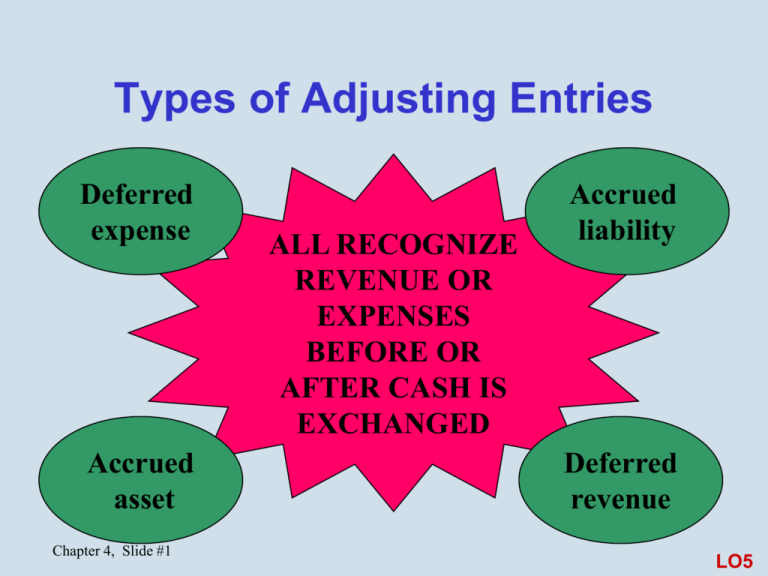
Types of Adjusting Entries Deferred expense Accrued asset Chapter 4, Slide #1 ALL RECOGNIZE REVENUE OR EXPENSES BEFORE OR AFTER CASH IS EXCHANGED Accrued liability Deferred revenue LO5 Accruals (deferred expenses) Cash paid before expense is incurred Examples: • Prepaid rent • Prepaid insurance • Office supplies • Property and equipment Costs are initially recorded as assets and allocated to expenses in future periods Chapter 4, Slide #2 Accrual Example Prepay rent on office space for one year on September 1 Initial journal entry: 9/1 Prepaid Rent 2,400 Cash 2,400 Monthly adjusting journal entry: 9/30 Rent Expense 200 Prepaid Rent 200 ($2,400 annual × 1/12 = $200 per month for 12 months) Chapter 4, Slide #3 Unearned (Deferred) Revenue Cash received before revenue is earned Examples: • Insurance collected in advance • Subscriptions collected in advance • Gift certificates Receipts are initially recorded as liabilities (unearned or refundable receipts) and recorded as revenues in future periods when earned Chapter 4, Slide #4 Deferred Revenue Example Received $2,400 for an insurance policy in advance on September 1 Initial journal entry: 9/1 Cash 2,400 Insurance Collected in Advance 2,400 Monthly adjusting journal entry: 9/30 Insurance Collected in Advance Insurance Revenue 200 ($2,400 annual × 1/12 = $200 per month for 12 months) Chapter 4, Slide #5 200 Accrued Liability Expense incurred before cash is paid Examples: • Payroll • Taxes • Interest Record expense (and corresponding liability) in period incurred; pay for it in a future period No cash flow on recording, only when paid Chapter 4, Slide #6 Accrued Liability Example #1 Pay biweekly wages of $28,000 At end of month, between pay periods: Wages Expense 4,000 Wages Payable 4,000 Next payday: Wages Payable Wages Expense Cash 28,000 Chapter 4, Slide #7 4,000 24,000 Accrued Liability Example #2 On March 1, assume a 9%, 90-day, $20,000 loan is taken out with a bank Initial journal entry: 3/1 Cash 20,000 Note Payable 20,000 Monthly adjusting journal entry: 3/31 Interest Expense 150 Interest Payable 150 ($20,000 principal × 9% × 3/12 = $450 for 3 months or $450/3 = $150 per month) Chapter 4, Slide #8 Accrued Asset Revenue earned before cash is received Examples: Revenue • Rent • Interest Record revenue (and corresponding receivable) in period earned; receive payment in a future period Chapter 4, Slide #9 Accrued Asset Example Rent payment of $2,500 due within first 10 days of month First day of the month: Rent Receivable Rent Revenue 2,500 Upon receipt of cash: Cash Rent Receivable 2,500 Chapter 4, Slide #10 2,500 2,500 Steps in the Accounting Cycle 1. Collect and analyze info 7. Close the accounts 2. Journalize transactions 6. Record and post adjusting entries 5. Prepare financial statements Chapter 4, Slide #11 3. Post transactions to general ledger 4. Prepare work sheet LO6