Skeleton Flip Book Info
advertisement

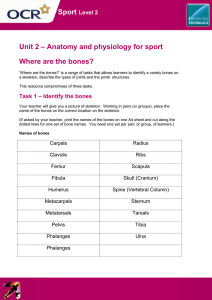
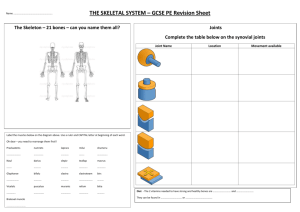
Function of Skeletal System 1. 2. 3. 4. Provides a framework. Allow Movement Provide Support Protect other parts of your body. 5. Form new blood cells 6. Store Minerals JOINTS A = Hinge (Elbow & Knee) move in one direction only. B = Gliding (Wrist & Ankle) enable bones to slide over one another. C = Pivot (Head & Neck) moves from side to side and up and down and allows limited rotation. D = Ball & Socket (Hip & Shoulder) move in all directions, allowing rotation. Scientific name – Common name PROBLEMS 1. Phalanges – fingers 1. Fracture- Break in a bone. 2. Metacarpals – hand (palm) 3. Carpals – wrist 2. Dislocation- When 4. Scapula – shoulder blade a bone is pushed out of its joint. 5. Rib – rib 6. Vertebrae – back bone (24) 3. Sprain- Stretching or twisting of 7. Pelvis – hip ligaments in a joint. 8. Patella – knee 9. Fibula – shinbone (smaller 4. Overuse injuriesHappen over time bone) and make up over 10. Metatarsals – foot (instep) half of the sports 11. Cranium – skull injuries in teens. Ex. Shin splints 12. Mandible – jaw 13. Clavicle – collarbone 5. Scoliosis14. Sternum – breastbone Sideways curvature of the 15. Humerus – upper arm spine. 16. Ulna – forearm (finger side) 17. Radius – forearm (thumb side) 6. OsteoporosisCondition with 18. Coccyx – tailbone brittle &porous 19. Femur – thigh bones due to 20. Tibia – shinbone (bigger deficiencies in calcium, vit. D, bone) certain hormones, 21. Tarsal – ankle and lack of 22. Phalanges – toes exercise. CARE 1. Be physically active 2. Eat foods high in calcium & phosphorus 3. Sit, stand, and walk with straight posture 4. Pay attention to your shoes- Shoes should provide correct arch support. Properly fitting shoes provide support for the bones of the feet. CONNECTIVE TISSUES 1. Cartilage- Example is nose and earStrong, flexible tissue that cushions joints. 2. Ligaments- Connect bones to bones at joints. 3. Tendons- connect muscles to bones at joints. Example Achilles Tendon