slides
advertisement

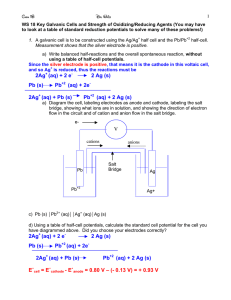
Electrochemistry By: Juan Mazzini and Liza Cohen Basic Info. Formulas • E = E◦ - (RT/ nF) ln(Q) • ∆G = ∆G◦ + RT ln(Q) • ∆G◦ = -nFE◦ Constants • F= 96500 C/Mole e- (C= coulombs) • R= 8.314 J*mol-1*K-1 Ideas for Red-Ox reactions • OXIDATION Loss of Electrons • REDUCTION Gain of Electrons • ** Reducing Agent = Substance being oxidized • ** Oxidizing Agent = Substance being reduced Procedures for balancing RXN • **Remember (charges) F= -1, O= -2, H= 1+ (except when hydride), pure elements = 0. • -Write properly balanced half reactions and get e- to cancel out. • - in acidic solution, add H+ and H2O • - in basic solution, do likewise. However, after balanced, add OH’s to form H2O’s. Sample Problems What is the oxidation state of each atom? • H2O • AsO4• Cr2O72- Sample Problem CH4 + O2 CO2 + H2O (unbalanced) • a. Determine which atom is oxidized and which is reduced. • b. Given that the cell reaction takes place in acidic solution, • i. write the two balanced half reactions that occur as the cell operates • ii. combine the two half reactions into an overall balanced reaction Electricity • -Reaction with greater potential is reduced. • -Reaction with smaller potential is flipped around (potential changes sign). • **Do not multiply by moles Voltage is independent of moles. • - E◦cell= E◦ox + E◦red • -Anode- substance being oxidized. Cathodesubstance being reduced. (vowels with vowels) • -e- flow from anode to cathode • -ions flow from cathode to anode • -oxidized: mass decreases • -reduced: mass increases From: www.sparknotes.com Sample Questions • • • • Mass increase/decrease? Direction of e-/ion flow? Location of anode/cathode? Determining the voltage Current • I = charge/ time = q/t • E= joules/ coulomb = J/C WHIN? (What Help is Needed) © Mr. John Charles Bruss