C3 Flash Cards - Groby Science

C3 Flash Cards
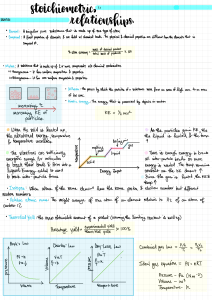
Measuring Rate of Reaction
• To measure rate you need weight/volume & time
• Calculate rate from gradient (y/x)
• Extrapolation: extend the graph
• Interpolation: predict within the graph
• Limiting Reactant: the reactant not in excess that is all used up
• Reaction stops when graph goes flat
Rate of Reaction
• Rate of reaction is faster when there is a faster rate of successful collisions
• Temperature: particles move faster
• Pressure: particles more crowded
• Surface area (powder): more particles available to react
• Concentration: more particles in the same volume
• Catalyst: increase the rate and is unchanged
Reacting Masses
• Relative Formula Mass (M r
)
• Add up masses from periodic table for each atom
• Multiply out brackets e.g. Ca(NO
3
)
2 means there are 6 Os
• Mass is conserved during a reaction
• Number of atoms on the left is the same as on the right
• Calculating Mass
• Work out M r for the substance your given the mass of and the substance you want to work out the mass of.
• Divide the mass of the substance whose mass you are given by it’s M r
.
• Multiply the answer by the M r of the substance you want.
Calculations
• Percentage Yield
• Actual yield_ x100
Predicted yield
• Want high % yield to reduce the reactants wasted & reduce cost
• Atom Economy
• M r of desired products__ x100 sum of M r of all products
• Want high atom economy to reduced unwanted products & be sustainable
Bond Energy
• Bond making is exothermic
• Energy given out
• Bond breaking is endothermic
• Energy taken in
• If a reaction is exothermic: more energy is given out than taken in
• If a reaction is endothermic: more energy is taken in than given out
Energy of Fuel
• Using a calorimeter
• Use spirit burner
• Heat water in copper calorimeter
• Measure: mass of water, mass of fuel burnt, temperature change
• Calculating energy transferred
• Energy transferred equation is given: use water numbers!
• Energy per gram = Energy released (J)_ mass of fuel burnt (g)
Batch or Continuous
• Batch: used for pharmaceutical drugs
• Can test regularly
• Can make in small amounts
• Drugs difficult to develop & test so that its safe to use
• Continuous: used for chemicals e.g. ammonia
• Extracting chemicals form plant sources
• Crush plant
• Boil & dissolve in suitable solvent
• Chromatography
• Match melting/boiling points to see if pure
Allotropes
• Made of the same element but with different structures: carbon
• Diamond
• Hard so used in cutting tools
• Shiny so used in jewellery
• No free electrons so can’t conduct electricity
• High melting point as has strong covalent bonds
• Graphite
• Layers so can be used as pencil lead & lubricant
• Has free electrons so can conduct electricity
• High melting point as strong intermolecular forces
• Fullerenes
• Spheres to use a drug delivery systems
• Nanotubes can attach catalysts to