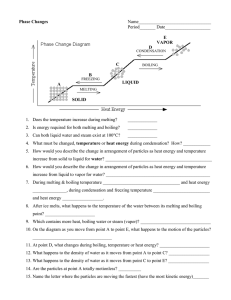
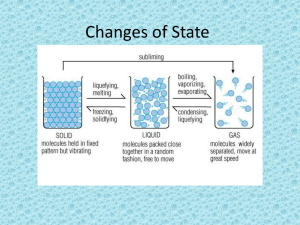
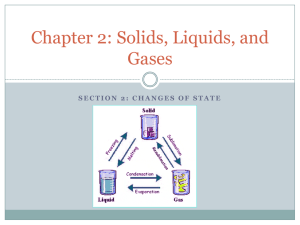
Changes of State: the change of a substance from one physical state
advertisement

Changes of State: the change of a substance from one physical state to another Energy’s Role in Changes of State • Physical change – The identity of the substance does NOT change • Particle Arrangement changes – The particles of a substance move differently depending on the state of the substance. Adding Energy • Melting occurs when energy is added to a substance – Melting: the change of state in which a solid becomes a liquid by adding energy – Particles must overcome some attraction to each other – Endothermic (endo- means inside) • Solid to liquid • Temperature increase – Melting point: the temp at which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid Removing Energy • Freezing occurs when energy is removed from a substance – Particles’ attraction must overcome the motion of the particles. • Liquid to Solid – Freezing point: the temperature at which liquid turns to a solid • Freezing is the reverse of Melting – Exothermic (exo- means outside) Evaporation: the change of substance from a liquid to a gas • Surface – Below boiling point • Boiling: is the change of a liquid to a vapor, or gas throughout the liquid – Pressure inside bubbles =atmospheric pressure – Boiling point: the temp at which a liquid boils • Atmospheric pressure: varies depending on the relation to sea level Condensation: the change of state from a gas to a liquid • Condensation point: the temperature at which the gas becomes a liquid • Particles Clump together – Attraction between them overcomes their motion • Energy is removed – Exothermic change Sublimation: the process in which a solid changes directly into gas • Particles go from being tightly packed together to being spread far apart • Attractions between particles must be completely overcome • Energy is gained • http://youtu.be/XIdX9woG7yI Temperature vs Change of State Temperature Change of State •The speed of the substance’s particle •Temperature change is secondary •Change of State occurs first Quiz… 1. What are two changes of state that are endothermic? 2. Do the particles of a substance move faster or slower as the substance is heated? 3. When water evaporates, has a chemical of physical change occurred?