General Biology Notes CH 12: TRANSLATION A.K.A. PROTEIN

General Biology Notes
TRANSLATION
A.K.A. PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
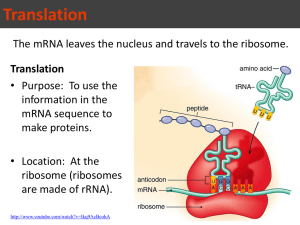
Translation Definition:
• the process of converting or translating the information in mRNA into a sequence of amino acids that makes up proteins.
NOTE:
• Before translation can begin, transcription of the DNA into mRNA must occur.
There are three types of RNA involved in protein synthesis:
mRNA, rRNA and tRNA
3 steps:
1. Initiation: mRNA attaches to the ribosome (rRNA). (The rRNA slides along the mRNA like a bead on a string.)
• rRNA “ reads ” the mRNA in groups of three nucleotides called a codon .
• Translation always begins with a special codon ( AUG ) called the initiator or start codon.
NOTE:
• there are 20 different amino acids and
64 different codons. Each amino acid may have more than one codon but each codon specifies for only one amino acid.
mRNA codon chart
2. Elongation :
• Transfer RNA (tRNA) carries or “ taxis ”a specific amino acid determined by the anticodon to the ribosome .
• The anticodon of tRNA pairs with the complementary codon on mRNA.
• As the tRNA’s line up the amino acids, peptide bonds form between amino acids linking them into a protein.
• The tRNA’s are recycled back to pick up more amino acids.
3. Termination :
• the protein is released from the ribosome when a “ stop ” codon is reached. There are three special “stop” codons: UAA,
UAG and UGA