Translation ppt

Does anyone remember what the differences between RNA and DNA are?
RNA
Has one strand
Has the sugar ribose
Has the base
Uracil (U)
Both
Made of nucleotides
Have 4 bases
Are nucleic acids
DNA
Has two strands
Has the sugar deoxyribose
Has the base
Thymine (T)
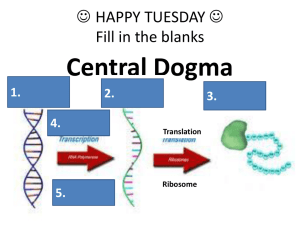
What does the enzyme RNA Polymerase do? What step of gene expression is this?
The Genetic Code: Three Letter Words
• A gene is like a
“sentence” of “words”
• After transcription, the mRNA “words” are carried out of the nucleus to the ribosome/cytoplasm
Codons of mRNA
• Each of the “words” are made up of 3 bases
• Each 3 base sequence is called a codon
• Each codon is matched to 1 of 20 amino acids or is a START or STOP signal
What amino acid does each codon represent?
• UUG = Leucine
• GUA = Valine
• CAC = Histidine
• ACU = Threonine
• AGG = Arginine
• CCG = Proline
Translation: RNA to Proteins
• Translation is the process of converting the
“language” of RNA into the “language” of proteins
• Translation occurs in a sequence of steps, involves 3 kinds of RNA, and results in a complete polypeptide (protein)
Step 1
Step 2
Translation: RNA to Proteins
Each tRNA has an amino acid and a 3 base sequence (anticodon) on the other end.
The anticodon is complementary to a specific codon on the mRNA.
mRNA leaves the nucleus and joins a ribosome. mRNA has a start codon: AUG.
A tRNA with the complementary anticodon UAC binds to the mRNA and begins the protein chain with the first amino acid: methionine.
A second tRNA binds to the next codon and delivers the next amino acid. A peptide bond is formed between the two amino acids and the first tRNA is released.
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Translation: RNA to Proteins
The ribosome moves down one codon, which allows another tRNA to bind to the next codon. The process repeats, lengthening the chain of amino acids.
The process repeats until a stop codon is reached. At that point, since no tRNA’s have the correct anticodon, no more amino acids are added to the chain. The 3
STOP CODONS are: UAG, UAA, and UGA
The protein falls off of the ribosome. The ribosome falls apart and becomes available to translate another mRNA sequence.
Translation
Translation Videos
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_6Rrymt6
XwI
DNA Translation Animation by Interact Medical
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=983lhh20r
GY
DNA Transcription and Protein Assembly