Protein Synthesis-Interactive Tutorial
advertisement

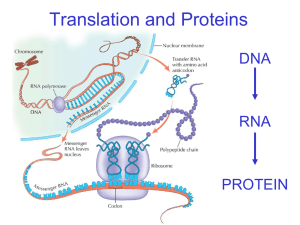
SBI4U0 Name ______________________ Protein Synthesis-Interactive Tutorial Answer the following questions as you work through the tutorial Overview: 1. What are the two stages of the Central Dogma? 2. What happens during transcription? Draw a sketch. 3. What happens during translation? Draw a sketch. Basics: 4. Complete the chart: Differences in protein synthesis between prokaryotes and eukaryotes Event Transcription Location in Prokaryotes Translation of membrane or secreted proteins Translation of other proteins 5. This tutorial will focus on which type of cell? 6. Three bases are referred to as _________________ 7. What are anticodons? Draw a sketch to illustrate. Location in Eukaryotes 8. What codon does translation always begin with? Which amino acid does this represent? 9. In what direction is the code read? 10. What does the stop codon do? What are the three stop codons? 11. The genetic code is degenerate. What does this mean? 12. Translate the code below. 13. What would happen if a single point mutation occurred as shown below? 14. What does it mean to have a gene expressed? Players: 15. Describe two differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic mRNA. 16. Describe the structure of the tRNA molecule. Incluse the following terms: anticodon, complimentary mRNA codons amino acid, covalent bond Include a sketch 17. What is the third major player in protein synthesis? 18. What are ribosomes composed of? 19. Which anticodon is the correct match for the MRNA triplet shown below? Big Picture: 20. mRNA is the template, what is the first thing that it must tell the rRNA? 21. What is the Shine-Delgarno sequence? Where is it found and what is it composed of? 22. What is responsible for the attachment of the first section of the ribosome to the mRNA? 23.What role does GTP play in fMet and IF? 24. What is the P site? 25. What is the A site? 26. What role does GTP play? 27. What happens after the IF (initiation factor) has been removed? 28. What is the first step of elongation? 29. The second step in elongation is the formation of what kind of bond between the amino acids? Which enzyme catalyzes the reaction? 30. The whole ribosome is then shifted down one codon. What is on the P site and what is on the A site? What happens to the empty tRNA? 31. Fully explain what happens when the ribosome comes to the stop codon UGA. 32. Label the following blanks: 33. For the translation of 125 amino acids polypeptide chain, how many GTP molecules are hydrolyzed. Explain how you arrived at the answer. 34. Circle the peptide bond in the proline/methionine chain below.