Translation
advertisement
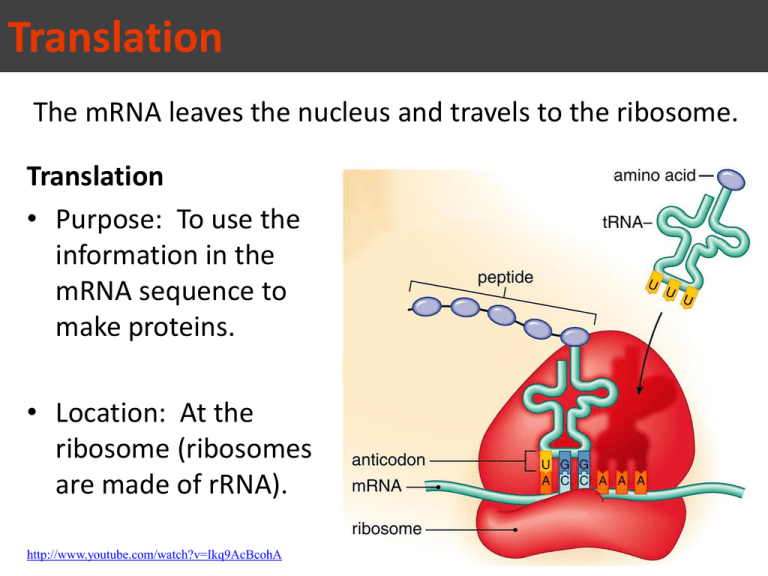
Translation The mRNA leaves the nucleus and travels to the ribosome. Translation • Purpose: To use the information in the mRNA sequence to make proteins. • Location: At the ribosome (ribosomes are made of rRNA). http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ikq9AcBcohA Translation Process: • The ribosome reads the mRNA 3 nucleotides at a time. • Codon: a group of 3 mRNA nucleotides that corresponds to a single amino acid. • Genetic Code: The sequence of nucleotides in DNA or RNA that determines the specific amino acid sequence in the synthesis of proteins. tRNA molecules Growing polypeptide Large subunit mRNA Small subunit http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5bLEDd-PSTQ Translation • Genetic Code – There are 64 different codon combinations (4 X 4 X 4 = 64). – There are only 20 different amino acids, so there is more than one codon for each amino acid. – Methionine is always the first amino acid in a protein. (AUG is referred to as a start codon) – There are three different stop codons which end translation. So if you give me a sequence of DNA can I figure out the exact sequence of amino acids? STEPS 1. Take the DNA and transcribe it into mRNA Example: mRNA: TAC ATA CTA GCG ACT AUG UAU GAU CGC UGA 2. Take the mRNA sequence and decode it using the codon chart. AUG = MET UAU = TYR GAU = ASP CGC = ARG Translation • Using the genetic code, the tRNA molecule brings the correct amino acids to the ribosome. • Each molecule of tRNA has 2 parts. – Anticodon: sequence of 3 nucleotides that matches up with an mRNA codon. – Amino acid: each tRNA molecule can bind to only a specific amino acid.