Translation PPT
advertisement
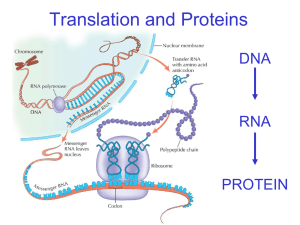
The Genetic Code and Translation • Codon – three mRNA bases in a row that code for an amino acid Divide this mRNA strand into codons: AUGGGCACUCUCGCAUGA ↓ AUG GGC ACU CUC GCA UGA • Genetic Code – chart used to determine which amino acid goes with a certain codon – Universal – all organisms use the same code – There are 64 different codons, but only 20 amino acids. (So, there may be more than one codon for an amino acid.) – AUG codes for methionine (the “start” codon) • Signals the beginning of protein production – UAA, UAG, UGA – “stop” codons • Signals the end of protein production (no amino acid) • Translation – mRNA is used to make a protein – Sequence of bases determine sequence of amino acids – Occurs at ribosomes Steps of Translation 1. mRNA attaches to ribosome 2. tRNA brings amino acids to ribosome - tRNA anticodon is complentary to mRNA codon 3. As ribosome slides down mRNA, more amino acids are brought by tRNA. 4. Amino acids form peptide bonds and fold to make the protein. http://passel.unl.edu/pages/animation.php?a=translation.swf DNA: mRNA: tRNA anticodons: Amino acids: TAC AGA CCC TTG CGG TCG ACT Translation Translation • • • • • • • A = amino acid B = tRNA C = anticodon D = codon E = mRNA F = ribosome G = protein Translation