11/13/12 Protein Synthesis Part II: Genetic Code and Translation
advertisement
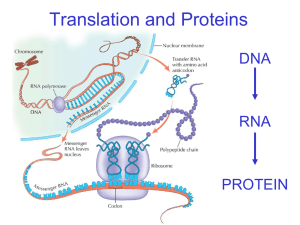
Protein Synthesis Part II: Genetic Code and Translation Which is single stranded? 7% 1. 93% 2. DNA RNA Where in the cell does transcription take place? 0% ol gi G ol e cu Va Bo d s le u uc N m 0% y 0% on dr ia 0% ito ch 5. M 4. la s 3. yt op 2. Cytoplasm Mitochondria Nucleus Golgi Body Vacuole C 1. 100% If a DNA strand has the following sequence of base pairs – A C T G G T C C A A , then the mRNA strand would have what 100% sequence? G ... A G C C C A U G U G T A C T C G C G U T A C G ... 0% ... 0% ... 0% C 4. A 3. G 2. TGACCAGGTT ACTGGTCCAA TGUCCUGGTT UGACCAGGUU T 1. mRNA is synthesized in the nucleus and travels to the cytoplasm to meet up with which organelle? 80% 13% 7% 0% N uc le u s e so m so Ly G ol gi so Bo d m e y 0% ib o 5. R 4. on dr ia 3. ito ch 2. Mitochondria Ribosome Golgi Body Lysosome Nucleus M 1. Genetic Code Quick Review of Proteins… Monomer: Amino Acid 20 different amino acids! The properties of proteins are determined by the order of the amino acids The Genetic Code! RNA contains 4 different bases: A, G, C, U The genetic code is read three letters at a time Each “word” of the coded message is three base pairs long These “words” are called codons RNA Sequence: UCGCACGGU Read sequence 3 bases at a time UCG – CAC – GGU Each set of three bases is a codon. Each codon represents a different amino acid …more genetic code AUG is the start codon In addition there are 3 different stop codons. Stop codons are like the period at the end of a sentence. Using your mRNA codon chart, what amino acid would a ribosome call for if the codon was A A C ? 13% 7% in e ro s Ty Ly e ar ag in sp A lu ta m G si ne 0% in e 0% in e 5. la n 4. yl a 3. 80% en 2. Phenylalanine Glutamine Asparagine Lysine Tyrosine Ph 1. Translation RNA and Ribosomes work together to produce proteins Transfer RNA For translation we need a new type of RNA Transfer RNA (tRNA) is responsible for carrying different amino acids to the ribosome. tRNA has a three base sequence called an anticodon Steps in Translation mRNA attaches to the ribosome tRNA brings in the amino acids Anticodons match with codons Peptide bonds form between amino acids Translation Translation continues until a stop codon is read The newly formed protein is released Where in the cell does translation, the second part of protein synthesis, take place? Mitochondria Nucleus Golgi body Cytoplasm 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 0% G 13 14 15 0% m la s yt op le u uc N ito ch 2 M 1 0% s on dr ia 0% 16 C 4. y 3. bo d 2. ol gi 1. 17 18 19 20 Molecules called tRNA’s are floating around the cytoplasm carrying what? mRNA’s Glucose DNA Nucleotides Amino Acids 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 16 s ds 0% 17 Ac i m in o N 1 0% A lu c G m 0% tid e os A’ s RN 0% e 0% le o 5. uc 4. A 3. N 2. D 1. 18 19 20 An mRNA codon is made up of how many nitrogen bases? 1 3 6 24 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 0% 3 0% 1 0% 13 14 0% 15 16 17 18 24 2. 6 1. 19 20 What protein would be synthesized from the following mRNA strand? ACUUUCGAAUAC 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 15 16 17 0% ni ne – cy ... gl u. .. – in e yl a re o en 14 Th 4 Ph 3 0% ... la n – ni ne re o 2 Th 1 0% in e ph 4. 0% ro s 3. Ty 2. ... Threonine – phenylalanine – glutamate – tyrosine Phenylalanine – leucine – methionine – valine Tyrosine – glutamate – phenylalanine – threonine Threonine – cysteine – arginine – histidine 1. 18 19 20