Schizophrenia
advertisement

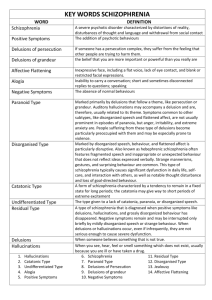
Schizophrenia Kimberley Clow kclow2@uwo.ca http://instruct.uwo.ca/psychology/155b/ Outline • What is Schizophrenia? – Positive Symptoms – Negative Symptoms – Subtypes – Phases • Development • Causes • Treatment What Is Schizophrenia? • Most severe of adult psychiatric disorders – Interferes with the ability to think, manage emotions, & relate to others • History – Kraepelin – Bleuler 1 Course of Schizophrenia Schizophrenia • Psychotic Disorder – Characterized by major disturbances in thought, emotion, and behaviour • Positive symptoms • Negative symptoms – 3 Main Clusters • Withdrawal • Magical Thinking • Disorganization Positive Symptoms • Excesses or Distortions • Disorganized or Catatonic Disorder • Disorganized Speech – Loose Associations – Tangential Thinking – Word Salad • Hallucinations • Delusions 2 • Types of Delusions – Persecutory delusions – Delusions of being controlled – Thought broadcasting – Thought insertion – Thought withdrawal – Delusions of guilt or sin – Somatic delusions – Grandiose delusions First of all thank you very much for your desire to help me. I am twenty eight years old Men. My specialty is theoretical physic, I have finished university in spite of the fact that deficit of conscious mental acts means sharp reduction of creative activity and on the other hand it very impedes social communications (I do not know how modern psychiatrists call my disturbance, thinking not clearly?). From childhood I was very active and creative boy, I studded in the physic and mathematical school and participated in many Olympiads. At the beginning reduction of psychic activity took place very slowly and mental exercise which required learning (for example studding of verses or text by heart) facilitate my deficit of subjective psychic activity but one day (in one second) occurred sharp lowering of intentionality. My age was sixteen years then and since my disturbance remains without any change. I was treated by best psychiatrist of my country and Russian. At the beginning they think I have depersonalization disorder but then they changed their opinion and now think that I have “schizophrenic ego-dysfunction”. Of course, they do not mean that I have schizophrenia. I tried risperidone and zyprexa and I am sure they cannot be effective for treatment my disturbance, moreover probably my disturbance is not linked with hypoactivity of the cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical network and as Andreasen thinks disturbance of creative activity is not characteristic for schizophrenia at all. There are not neither books nor journals in my country, I have read only abstract of your article from Behavioral and Brain Science and decided to ask you advice. Negative Symptoms • • • • • Blunted Affect Alogia Avolition Impaired Social Skills Withdrawal & Antisocial • Anhedonia 3 Development of Schizophrenia • Process Schizophrenia • Reactive Schizophrenia – Chronic – Slow onset, develops gradually over time – evidences of oddity from early in childhood – poor prognostic outlook – Acute – Sudden and dramatic onset marked by intense emotional and intellectual upheaval – Diathesis-Stress Model Phases of Schizophrenia Subtypes • Are there really subtypes? • Seem to be some grouping of symptoms – Disorganized – Catatonic – Paranoid • Other categories – Undifferentiated – Residual 4 What is Going On? Eye Tracking • Excessive amounts of dopamine in frontal lobes • Differences in Processing Information – Novelty processing – Difficulty inhibiting stimuli – Smooth pursuit eye movements disrupted Myths • False assumptions about schizophrenia – – – – – Violence Multiple personalities Homelessness Due to frigid mother Due to conflicting messages – Due to conflict resolution in relationships – Sex abuse Causes • Biology – Genetics • Heritability – Neurotransmitters • Dopamine – Abnormal brain structures – Infection 5 • Psychological Stress – Social Class • Sociogenic Hypothesis • Social Selection Theory – Cannabis – The Family • Expressed Emotion (EE) Treatment • Biological – Antipsychotic Drugs • Akinesia • Akathesis • Tardive Dyskinesia • Cognitive-Behavioural Therapy – Target bizarre behaviour – Counter irrational thoughts – Social-Skills Training • Family Therapy – Attempt to reduce expressed emotion • General Trends – Families and patients can be given realistic and scientifically sound information – Medication is only part of treatment – Early intervention affects course and treatment – Integrated treatment is not widely available 6 Concluding Remarks • It is an all consuming disorder – Thoughts, feelings & behaviour • Drug therapy is most common – Nasty side-effects – Life-long treatment • With current treatments – About 25% of schizophrenics recover fully – About 10% have chronic deterioration – About 65% have partial recoveries 7