Meiosis
advertisement

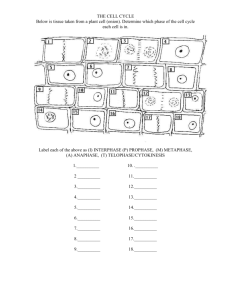
Topics: 3 & 10 4.2 & 10.1 Meiosis • What is the difference between meiosis and mitosis? 1 – Meiosis Preparation Read & Consider Understandings 3.3.1-3.3.3 & 10.1.1 In meiosis four daughter cells are produced and each has half of the original number of chromosomes and is said to be haploid (n). meiosis consists of two nuclear divisions of a diploid nucleus (2n) and only one replication Meiosis Halving the number of chromosomes in gametes allows for fusion of gametes and a genetically unique individual. Sexual Life Cycle Diploid (2n)= 4; Haploid (n) =2. INTERPHASE 4.2.3 Outline the process of meiosis, including pairing of homologous chromosomes and crossing over, followed by two divisions, which results in four haploid cells. • Define homologous chromosome and sister chromatid. 2 – Meiosis Steps Read & Consider Understandings 3.3.4-3.3.6 & 10.1.5-10.1.6 Homologous chromosomes are the same length, have the same shape and carry the same genes at the same gene loci. Meiosis I: This is the first of two sets of divisions. This division separates homologous pairs. PROPHASE I Prophase resembles prophase in mitosis in that the nuclear membrane breaks down, spindle fibers form, and chromatids condense. Crossing-over Metaphase I Anaphase I TELOPHASE I This completes the reduction division and each cell has one of the pair of homologous chromosomes, but still two identical copies of each. Meiosis II: involves the separation of the sister chromatids and looks very much like mitosis. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes separate; in meiosis II sister chromatids separate. Draw and label the stages of meiosis. • How is individual uniqueness achieved? 3 – Genetic Variation Read & Consider Understandings 3.3.7-3.3.8, 10.1.2-10.1.4 & 10.1.7 The point at which homologous chromosomes join by ‘crossing over’ is known as the chiasma It is common to have at least one or more chiasmata between homologous pairs. Crossing Over Variation Independent assortment of maternal and paternal homologous chromosomes in metaphase I. Crossing over of segments of individual maternal and paternal homologous chromosomes. Allele pairs (homologous chromosomes) separate independently during the formation of gametes Traits are transmitted to offspring independently of one another Mendel’s Law The law of independent assortment is accomplished during metaphase I. Allele pairs separate independently because of the random orientation of homologous chromosomes when they align. Independent Assortment Non-disjunction is the failure of homologous chromosomes to separate during anaphase I. Resulting in too many or too few chromosomes in a particular gamete. Non-Disjunction Chorionic villus sampling Amniocentesis Karyotyping "CELL DIVISION: MEIOSIS AND SEXUAL REPRODUCTION." Estrella Mountain. N.p., n.d. Web. 13 Aug. 2015. "Meiosis: Crossing Over and Variability [3D Animation]." YouTube. YouTube, 5 Mar. 2014. Web. 13 Aug. 2015. Sadava, et al., Life: The Science of Biology, Ninth Edition, Sinauer Associates © 2010 Sinauer Associates, W. H. Freeman & Co., and Sumanas, Inc. Works Cited