Major Laws Imposed by British Government What the Law Said How
advertisement

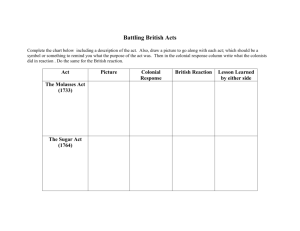
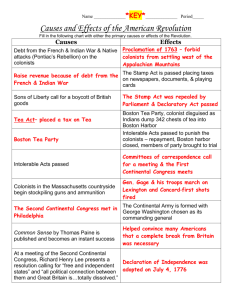
Major Laws Imposed by British Government Proclamation of 1763 Sugar Act of 1764 Quartering Act of 1765 Stamp Act of 1765 What the Law Said British troops were stationed in America to protect the British empire. The law attempted to restrict colonial settlement west of a certain point in the Appalachian Mountains. Lowered the tax on molasses imported by the Colonists. British officers were allowed to seize goods from smugglers without going to court. Required Colonists to provide food and housing for the British troops stationed in the colonies. Tax stamps were required on items such as newspaper, wills, cards, dice, calendars, and most legal documents. The Stamp Act was repealed in 1766. How the Colonists Reacted How did it lead to the American Revolution Major Laws Imposed by British Government Townshend Act of 1767 Tea Act of 1773 Intolerable/Coercive Act of 1774 What the Law Said Approved the use of Writs of Assistance. Did not allow meetings of the New York legislature until the Quartering Act was obeyed. Placed import taxes on paper, paint, glass, lead, and tea. Provided that some of the revenue (money) collected was to be used to pay the salaries of British officials and to prevent smuggling. Lowered the tax on tea, but granted the British owned East India Company a monopoly, or complete control, over the sale of tea. Closed the port of Boston to trade until payment was made for the tea destroyed during the Boston Tea Party. Directed that British officials charged with serious offenses in the line of duty would be sent to England or another colony for trial. Restricted the holding of town meetings and drastically reduced much of Massachusetts self-government. Forced Colonists to house British troops. How the Colonists Reacted