British Acts & Taxation
advertisement

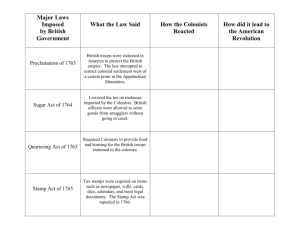
British Acts & Taxation on Colonies 1. Writs of Assistance search warrants designed to limit illegal smuggling of goods into the colonies from other nations, argued to be contrary to natural law (James Otis) 2. Sugar (Revenue) Act (1764) designed to raise revenue through taxes on imported goods, violators were tried before admiralty court w/o due process of jury 3. Quartering Act Required Americans to pay/provide for British soldiers stationed in colonies 4. Currency Act (1764) forbade currency not redeemable in gold or silver, made it difficult for colonists to avoid money drains that British mercantile policies were supposed to create 5. Stamp Act (1765) o first direct tax on Americans required Americans to purchase revenue stamps on any documents or paper products o short-sighed, overlooks mercantilist advantage already provided by British economy 6. Declaratory Act (1766) o passed with the repeal of the Stamp Act o states that Britain can tax Americans "in all cases whatsoever", thereby eliminating American right to no taxation without representation 7. Townshend Duties o creates Admiralty Courts to try violations, use of Writs of Assistance, paying customs officials out of the fines levied o suspended New York legislature for noncompliance with the Quartering Act 8. Tea Act (1773) o British East India Company gets permission to ship tea directly to the colonies rather than through Britain (Americans are smuggling in Dutch tea, hurting BEI Company) o British tea would be cheaper, even with the tax, than smuggled tea, hope that Americans will accept Britain's right to tax them o Americans strongly resist, sometimes don't even allow tea ships to land 9. Coercive Acts o known in colonies as the "Intolerable Acts" o set of four acts under one title o Boston Port Act closes Boston harbor until colonists pay for lost tea (which they don't) o Massachusetts Government Act increases power of the royal governor at the expense of the legislature o Administration of Justice Act allows royal officials convicted of crimes to be tr ied in Britain, greater chances of aquittal o Quartering Act (2nd) allows Gen. Thomas Gage (governor) to quarter troops anywhere, including private/unoccupied homes o