States_of_Matter
advertisement

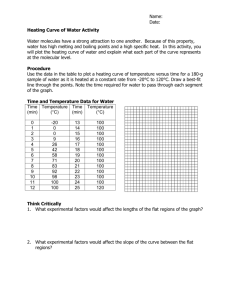
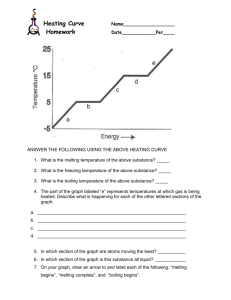
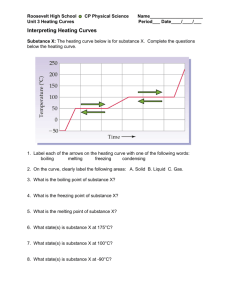
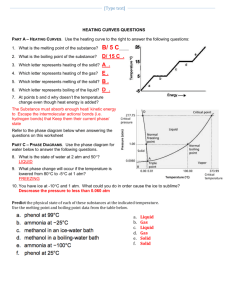
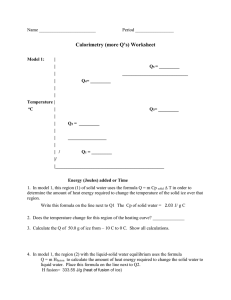
The Energy Associated with Phase Changes Sarah Longstaff Carol Murphree Stacie Williams Learning Objectives State and describe the three states of matter. Using kinetic molecular theory (KMT), explain the similarities and differences between each phase. Using KMT, describe what happens within each phase and the transitions between phases. Define heat and describe how it is measured. Draw the heating curve of a given substance by plotting temperature as a function of time. From an energy point of view, explain the heating curve. Learning Objectives • • • • Explain how heat is involved in phase transitions. Define heat capacity, specific heat, heat of fusion, and heat of vaporization. Experimentally determine the values for heat capacity, specific heat, heat of fusion, and heat of vaporization of a given substance. Given the values for heat capacity, specific heat, heat of fusion, and heat of vaporization, determine the amount of heat involved in a specific phase transition. Alignment with Massachusetts Chemistry Frameworks Identify and explain some of the physical properties that are used to classify matter. e.g. … melting point, and boiling point. (1-1) Describe the four states of matter (solid, liquid, gas, plasma) in terms of energy, particle motion, and phase transitions. (1-2) Analyze the energy changes in physical and chemical processes using calorimetry. (10-3) Lesson Plan Goal Introduction This unit incorporates the Virtual Molecular Dynamics Laboratory (VMDL) to compliment the traditional study of the states of matter. It allows students to visualize the behavior of solids, liquids, and gases on the molecular level. Lesson Plan – Day 1 Introduction to states of matter and their transitions. Background reading assignment. Teacher guided worksheet. Assignment of problem sets. Lesson Plan – Day 2 Simple assessment to determine any prior misconceptions and prior knowledge. Introduction/Review of kinetic molecular theory (KMT). Simulab: Explore the Common States of Matter. Provide rubric for unit project and if possible exemplars. Lesson Plan Day - 3 Laboratory: Boiling Point. SMD simulation of boiling. Compare simulation with laboratory. Data manipulation and analysis. Students will collaborate (teacherassigned teams) to interpret data. SMD Movie: Boiling Lesson Plan Day - 4 Teacher-directed discussion of heat and temperature. Demonstration/Minilaboratory: Heat and the Calorie. Demonstration/Minilaboratory: The Energy in a Nut. Lesson Plan Day - 5 Laboratory: Melting Point Determination. SMD simulation of melting SMD Movie: Melting Lesson Plan Day - 6 Construction and discussion of the heating curve. Introduction to heat capacity, heat of vaporization, and heat of fusion. Lesson Plan Day - 7 Heating curve assessment. Laboratory: Heat of Fusion of Ice. Lesson Plan Day – 8 and 9 Introduction to specific heat. Laboratory: Specific Heat of Liquids. Laboratory: Specific Heat of Solids. Lesson Plan Day - 10 Teacher modeled laboratory calculations for the heating curve. Simulab: Heating Curve. Draw connections between previous laboratories and the final heating curve. Lesson Plan Day - 11 Review calculations. Provide clarification for unit project. Make connections between all activities by generating a graphic organizer with the class. Lesson Plan Day - 12 Unit exam incorporating several assessment tools to assess all types of learners. Questions will include free response, calculations relating to laboratory, and multiple choice type questions. Collect unit project. Lesson Plan Analysis Material presented in logical sequence. Prior knowledge and misconceptions assessed. Frequent assessments to gauge student comprehension/mastery. Assessment and instruction designed to target all types of learners. Several hands on activities to engage students. Unit project to make connections. Special Thanks To Sergey Buldyrev Lidia Braunstein Mary Shann BU CPS