Long-Term Objectives

Topic 4
Long-Term Objectives and
Grand Strategies
Topics
• Long-Term Objectives
• Generic Strategies
• Grand Strategies
Long-Term Objectives
…
Examples
Statements of the results that a firm seeks to achieve over a specified period
• Profitability
•
Productivity
• Competitive position
• Employee development
• Employee relations
• Technological leadership
•
Public responsibility
Qualities of Long-Term Objectives
Achievable
Understandable
Suitable
Criteria used in preparing objectives
Motivating
Acceptable
Flexible
Measurable
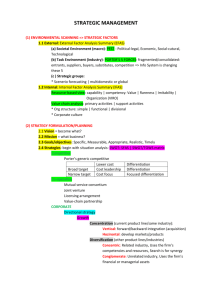
Porter’s Generic Strategies core ideas about how the firm can best compete in the marketplace … based on either …
Differentiation
Low-cost Leadership
Focus
(Niche)
Porter’s
- Requirements for Generic
Competitive Strategies
Generic
Strategy
Commonly Required Skills and
Resources
Common Organizational
Requirements
Overall Cost
Leadership
• Sustained capital investment and access to capital
• Process engineering skills
• Intense supervision of labor
• Products designed for ease in manufacture
• Low-cost distribution system
• Tight cost control
• Frequent, detailed control reports
• Structured organization and responsibilities
• Incentives based on meeting strict quantitative targets
Foundation Strategy
Broad Cost Leader
… will attempt to be the low-cost producer in both segments of the market. It will have good profit margins on all sales while keeping prices low for price-sensitive customers.
Firm Profile:
• More likely to reposition products than introduce new ones to the market
• Capacity improvements are unlikely to be undertaken (may run overtime instead)
… Automation may be pursued to increase margins
• Investments will be financed with debt and/or stock issues
• Tends to spend less on promotion and sales
• Focus on Market Share, Profits, and Stock Price
Foundation Strategy
Cost Leader with Product Life Cycle Focus
… minimize costs through efficiency and expertise.
Products will be allowed to age and change in appeal from
High Tech to Low Tech buyers.
• Low R&D spending (very little repositioning & new product every 2-3 years)
• Invests in automation early in the product’s life-cycle
• Moderate spending on promotion and sales
• Focus on ROE, ROS, and Profits
Porter’s
- Requirements for Generic
Competitive Strategies
(contd.)
Generic
Strategy
Differentiation
Commonly Required Skills and resources
• Product engineering
• Creative flair
• Strong capability in basic research
• Corporate reputation for quality or technological leadership
• Unique combination of skills
• Strong cooperation from channels
• Strong marketing abilities
Common Organizational
Requirements
• Strong coordination among functions in
R&D, product development, and marketing
• Subjective measurement and incentives instead of quantitative measures
•
Amenities to attract highly skilled labor, scientists, or creative people
Foundation Strategy
Broad Differentiation
… will seek to create maximum awareness and brand equity. It wants to be well known as a maker of high quality/highly desirable products.
• Firm Profile:
• High R&D spending to keep products fresh
• Maintains a presence in both market segments
• Spends heavily on advertising and sales to create maximum awareness and accessibility
• Prices tend to be higher
• Focus on Market Share, Profits, and Stock Price
Foundation Strategy
Differentiation Strategy with a Product Life Cycle Focus
… seeks to be well-known as a top producer of good performing products in both segments.
Firm Profile:
• Multiple product lines in both segments
• High promotion and sales investments to create maximum awareness and accessibility
• High R&D expenditures to continually reposition product lines and keep products fresh
• Unlikely to invest in increased automation or production capacity
• Focus on ROA, Stock Price, and Asset Turnover
Porter’s
- Requirements for Generic
Competitive Strategies
(contd.)
Generic
Strategy
Commonly Required Skills and resources
Common Organizational
Requirements
Focus Combination of above policies directed at the particular strategic target
Combination of above policies directed at the particular strategic target
Foundation Strategy
Niche Cost Leader
… seeks to dominate the price sensitive Low Tech market segment. Its aim is to set prices below all competitors — and still be profitable.
Firm Profile:
• Multiple product lines in the Low Tech segment
• Invests heavily in automation
• Spends moderately on advertising to cost sensitive customers
(sales people have more than one product to pitch to prospects)
• Investments financed with debt and/or stock issues
• Focus on ROS, ROE, and Profits
Foundation Strategy
Niche Differentiation
… company seeks to be known far and wide as the top producer of the best performing state-of-the-art products.
Firm Profile:
• Multiple product lines in the High Tech Segment
• Minimum focus in the other segment
• High promotion and sales investments to create maximum awareness and accessibility
• High R&D expenditures to continually introduce new product lines and keep existing products fresh
• Unlikely to invest in increased automation or production capacity
• Focus on ROA, Asset Turnover, and ROE
Grand Strategies
Comprehensive general approaches that guide a firm’s major actions
• Concentrated growth
• Market development
• Product development
• Innovation
• Horizontal integration
• Vertical integration
• Concentric diversification
• Conglomerate diversification
• Turnaround
• Divestiture
• Liquidation
• Bankruptcy
• Joint ventures
• Strategic alliances
Characteristics of a
Concentrated Growth Strategy
• Involves focusing resources on the profitable growth of a single product , in a single market , with a single dominant technology
•
Rationale
– Firm develops and exploits its expertise in a limited competitive arena
Strategies of Market and Product
Development
• Market development
• Consists of marketing present products, often with only cosmetic modifications to customers in related market areas by
• Adding channels of distribution or
• Changing content of advertising or promotion
• Product development
• Based on penetrating existing market by
• Incorporating product modifications into existing items or
• Developing new products connected to existing products
Innovation Strategy
Involves creating a new product life cycle, thereby making similar existing products obsolete
Horizontal and Vertical Integration
Strategies
Horizontal Integration
• Based on growth via acquisition of one or more similar firms operating at the same stage of the productionmarketing chain
Vertical Integration
• Involves acquiring firms that
• supply acquiring firm with inputs ( backward integration) or
• are customers for firm’s outputs ( forward integration)
Diversification Strategies
Concentric Diversification
• Involves acquisition of businesses related to acquiring firm in terms of technology, markets, or products
Conglomerate Diversification
• Involves acquisition of a business because it represents a promising investment opportunity
• Primary motivation is profit pattern of venture
• Difference between the approaches
• Concentric diversification emphasizes commonality whereas conglomerate diversification emphasizes profits for each individual unit
Turnaround Strategy
Involves a concerted effort over a period of time to fortify a firm’s distinctive competencies, returning it to profitability done through :
Cost reduction
Asset reduction
Divestiture and Liquidation Strategies
Divestiture Strategy
• Involves selling a firm or a major component of a firm
• Reasons for divestiture
• Partial mismatches between acquired firm and parent firm
• Corporate financial needs
• Government antitrust action
Liquidation Strategy
• Involves selling parts of a firm, usually for its tangible asset value and not as a going concern
The Strategy of Bankruptcy
• Two approaches
•
Liquidation
– Involves complete distribution of a firm’s assets to creditors, most of whom receive a small fraction of amount owed (7)
• Reorganization – Involves creditors temporarily freezing their claims while a firm reorganizes and rebuilds its operations more profitably (11, 13)
Corporate Combination Strategies
Joint Ventures
• Involves establishing a third company (child), operated for the benefit of the co-owners (parents)
Strategic Alliance
• Involves creating a partnership between two or more companies that contribute skills and expertise to a cooperative project
• Exists for a defined period
• Does not involve the exchange of equity