Strategy - Hodder Education
advertisement

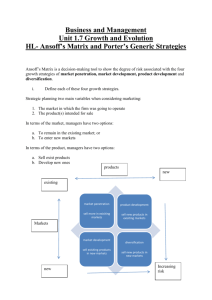
Business strategy Business strategy What is strategy? A business strategy is the means by which a business sets out to achieve its desired objectives. It can be described as the long-term plan of a business. Typically a business strategy will cover a period of the next 3–5 years and look to set out the overall direction of the business. Business strategy Types of strategy There are two main categories: (1) generic (general) strategies (2) competitive strategies Business strategy Generic strategies The main types of generic strategies that a business may use are: (1) Market dominance through internal growth (e.g. expanding assets) and in developing new products, and acquisitions (mergers and takeovers). (2) Globalisation i.e. moving operations into more and more countries. For example, Whole Foods entering the UK market. (3) Retrenchment involves cutting back to focus on your best lines. The Americans refer to this as ‘sticking to the knitting’. (4) Restructuring: a complete rethink of the way the business is organised using a range of techniques such as delayering (which involves flattening the management structure, removing bureaucracy and speeding up decision making). Business strategy Competitive strategies Competitive strategies are concerned with doing things better than rivals. There are two main ways of being competitive: (1) Cost leadership: selling goods at lower prices than rivals. This is possible when a firm is the market leader and benefits from economies of scale. (2) Differentiation: making your product different from competitors enables you to charge a higher price if desired. For example, the airline industry is divided into two main segments. At one end of the market are the premium price firms such as Virgin and Emirates that concentrate on differentiation. They offer better service to passengers, more legroom and better in-flight entertainment. At the other end of the market the emphasis is on being the lowest-cost producer, exemplified by ‘no frills’ airlines such as easyJet and Ryanair. Ryanair focuses on short-haul destinations and keeping its planes in the air as frequently as possible in a 24 hour period. Business strategy Theorist: Porter’s generic model Porter argued that there are two major strategies a business should focus on: (1) Cost leadership: be the cheapest and most cost-effective product. (2) Product differentiation: your product is the most innovative and different on the market. This attracts customers and generates large profits. Porter argued that the big danger is that a firm is both moderate in terms of cost and moderately differentiated — this attracts few customers to the product. It is better for the business to focus on one of the two strategies. Business strategy Theorist: Ansoff’s matrix Ansoff’s matrix suggests four alternative marketing strategies that hinge on whether products are new or existing. They also focus on whether a market is new or existing. Within each strategy there is a differing level of risk. Business strategy Market penetration Market penetration is about increasing the market share of an existing product. It is the most common type of strategy, as it is usually the safest. This is because the business already has the expertise and experience in the sector. A typical example would be a business using promotional offers such as buy one get one free (BOGOF) to increase sales and therefore market share. Business strategy Market development Market development is a little more risky, as it involves finding new markets for existing products. A business can do this by: • repositioning a product • moving into new markets (geographical) An example is Cobra Beer in the UK. Initially it was only sold in Indian restaurants, but the strategy of its owner was to expand into the airline, supermarket and pub markets. Whole Foods entering the UK market is another example. Business strategy Product development Product development is riskier still. This is because you are looking to develop a new product in an existing market, and product development is time consuming, lengthy and expensive in terms of research and development. For example, Tesco developed the Tesco Express brand in the UK market. It had the same customers but was a new product for Tesco. Innovation is key and this can be profitable if the right product is developed e.g. Dyson vacuum cleaners. Business strategy Diversification This involves moving new products into new markets. It is the most risky strategy. The more an organisation moves away from what it has done in the past, the more uncertainties are created. However, if existing activities are threatened, diversification helps to spread risk.