strategic analysis - Cal State LA
advertisement

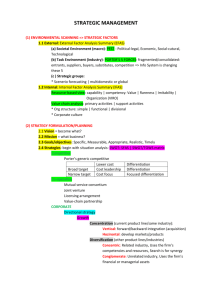
THE STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT PROCESS [or How to Analyze a Case] Dr. Laura Whitcomb Mgmt 497 Strategic Management Definition = The process whereby managers establish an organization’s long-term direction. This involves: 1) Setting Mission & Goals 2) Strategy Formation --internal capabilities --external environment --selection of strategy 3) Strategy Implementation 4) Strategy Evaluation How to Analyze a Case • • • • • Mission/Vision & Objectives Current Strategy Industry Analysis S.W.O.T. Analysis Recommendations MISSION Defined Answers the question “What business are we in?” or “Why do we exist?” --Customer Needs: What is being satisfied? --Customer Groups: Who is being satisfied? --Distinctive Competencies: How are customer needs being satisfied? Pepsico vs. Coke? • To be the world's premier consumer products company focused on convenient foods and beverages. • To Refresh the World...in body, mind, and spirit. • To Inspire Moments of Optimism... through our brands and our actions. • To Create Value and Make a Difference... everywhere we engage. Vision Statements • Future-oriented; transformative • Mission = what is; vision = what will be • Companies may have mission or vision or both • Mission and/or vision often accompanied by statement of company values GOALS = a desired future state that a company attempts to realize. Should be: - precise & measurable - addressing important issues - challenging but realistic - set for a specific time period - consistent with each other Types of Goals • Financial – Profitability – Revenue growth – Long-term shareholder value • Customer – Product/service attributes; relationship; image • Internal Process – Operations, customers, innovation – Corporate social responsibility • Learning & growth – Human, information, & organization resources Levels of Strategy & Organization Structure • Corporate Strategy ------>Corporate Head Office • Business Strategy ------>Business Divisions • Functional Strategy ------>R&D, HR, Finance, Operations, Marketing/Sales Corporate Strategy Generic Alternatives/Grand Strategies • • • • Stability Expansion Retrenchment Combination Expansion/Retrenchment Generic Choices • How? – Internal – External – Alliances • What? – Vertical integration – Horizontal integration – Diversification: related/unrelated Nestle’s Corporate Strategy • 2001 Acquired Purina pet food • 2002/5 Acquired Dreyer’s Ice Cream • 2006 Acquired Novartis nutrition business & Jenny Craig diet products • 2007 Acquired Gerber baby foods Porter’s Generic Competitive Strategies Purpose: achieve above-average long-run ROI for your industry. • Competitive Advantage – Cost Leadership – Differentiation • Competitive Scope – Broad Target – Narrow Target (Focus/Niche) Porter’s Generic Competitive Strategies Competitive Advantage/ Scope Lower Cost Differentiation Broad Target Cost Leadership Differentiation Narrow Target Cost Focus Focused Differentiation Tesla Goals & Strategy (summer 2007) Auto co. based in Silicon Valley • Begin producing $98,000 electric sports car in Oct. 2007 • Tesla engineers focus on the battery, computer software, & proprietary motor; outsource the rest – Uses lithium ion batteries, used in laptops, vs. nickel metal hydride – Development center in Detroit, with engineers hired away from Big 3 • Future: Sedan called White Star, $55-68,000; in 5 years, Blue Star, $30,000 Corporate Culture = Collection of beliefs, expectations, and values learned and shared by members and transmitted from one generation of employees to another. = Collective mental programming. Functions of Corporate Culture • • • • Conveys a sense of identity Generates employee commitment Adds to organizational stability Serves as a frame of reference Industry Analysis: Porter’s 5 Competitive Forces Purpose: understand why some industries have higher profit margins & what factors can change long-run industry profitability. • • • • • Risk of New Entry Rivalry Among Established Firms Bargaining Power of Buyers Bargaining Power of Suppliers Threat of Substitute Products ENTRY Barriers • Brand Loyalty • Absolute Cost Advantages – patents – access to raw materials – superior production techniques • Economies of Scale • Government Regulation Factors Affecting Intensity of RIVALRY • Competitive Structure – number of firms – relative market share • Demand conditions – growth – decline • Exit barriers Factors Affecting BARGAINING POWER • Number of firms in buyer vs. supplier industries • Quantity or % of total orders • Switching costs • Standardization vs. specialization of input • Threat of vertical integration SUBSTITUTES = products from OTHER industries that serve consumers’ needs in a way that is similar to those being served by your industry. Example: coffee vs. tea vs. soft drinks NOTE: Substitutes are very difficult to monitor, because they can involve technological changes in industries that did not pose any threat in the past. Company Situation Analysis • INTERNAL: Strengths & Weaknesses – financial position: relative & changes over time – functional capabilities: sustainable? distinctive? • EXTERNAL: Opportunities & Threats – demographic & socio-cultural changes – economic & political/legal changes – industry & technological changes RECOMMENDATIONS Shift from Analysis--->Synthesis • Is a fundamental shift in strategy required or not? • How do your recommendations line up with your SWOT analysis? • Is this a feasible, creative solution that is supported by your analysis?