molecular_compounds
advertisement

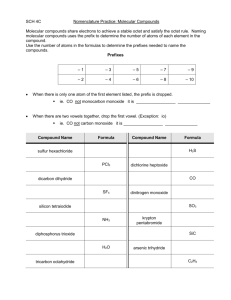
Science 10 MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS What is a molecular compound? A substance made up of molecules that is only composed of nonmetals They are different from ionic compounds because those are made up of a metal and nonmetal Electrons are shared between nonmetals to form a covalent bond The simplest molecules are diatomic (composed of two nonmetals) Ex. Cl2 Other molecules are composed of different nonmetals Ex. C6H12O6, H2O How to Write the Formula of a Molecular Compound The number of electrons that a nonmetal can share is called its combining capacity When predicting the formula of a molecule, use the combining capacity (group number) of the nonmetal Ex. C = group 14 (loss of 4 e-), O = group 16 (gain of 2e-) C4O2 C2O4 These formulas are not reduced Combining Capacities of Nonmetals 4 3 2 1 H C N O F Si P S Cl As Se Br I Naming Molecular Compounds Instead of using the ionic compound naming rules, we use the prefix system to name molecules Prefix Number Example mono- 1 carbon monoxide (CO) di- 2 carbon dioxide (CO2) tri- 3 carbon trioxide (CO3) tetra- 4 carbon tetrafluoride (CF4) penta- 5 phosphorous pentafluoride (PF5) Some Rules to Remember If there is not a subscript on the first nonmetal, the prefix mono does not have to be used If there are subscripts on both nonmetals, use prefixes for both Use the common name for the compound when applicable Ex. H2O is dihydrogen monoxide but you can call it water