MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
advertisement

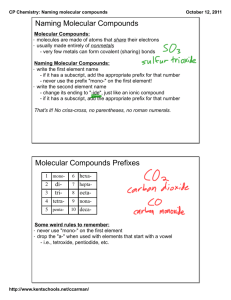
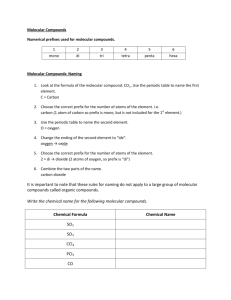
(2.2) MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS (p130-131) Naming and all that. Molecular Compounds Molecular compounds are formed by combining two non-metals. They do so by “sharing” electrons. The bond formed by sharing electrons is called a covalent bond. Properties of Molecular Compounds Often soft, liquid, solid or gas. If they dissolve in water, they form solutions that do no conduct electricity. Tend to have relatively low melting points. Naming Molecular Compounds Naming molecular compounds is different than naming ionic compounds because non-metals can combine in many different ways. Naming Molecular Compounds Eg. carbon and oxygen can combine 2 different ways!!! carbon monoxide CO carbon dioxide CO2 Naming Molecular Compounds To name a molecular compound prefixes are used to show the number of each type of atom. Prefix system Prefix Number mono 1 di 2 tri 3 tetra 4 penta 5 hexa 6 hepta 7 octa 8 nona 9 deca 10 Examples name formula sulfur trioxide dihydrogen monosulfide SiO2 CF4 N2O5 disulfur dinitride Examples name formula sulfur trioxide SO3 dihydrogen monosulfide H2S silicon dioxide SiO2 carbon tetrafluoride CF4 dinitrogen pentoxide N2O5 disulfur dinitride S2N2 NOTE: never have 2 vowels in a row between the prefix and element ex: 2 “o’s” monooxide Naming Molecular Compounds A molecular compound has a two-part name: first Non-metal Uses prefix for number Keeps its name second Non-metal Uses prefix for number Changes ending to “ide” Common Molecular Compounds You must know these…. H2O water H2O2 hydrogen peroxide CH4 methane CO2 carbon dioxide Practice -Video to recap! -Do: Worksheet 2.2 (C) - NAMING MOLECULAR COMPOUND PRACTICE -Quiz-Molecular Compounds next class TEST UNIT 1-Part A on THURSDAY! Classwork Workbook - 46-48 - 50-52 Worksheet 2.2 (D)-naming ALL! REMINDER: TEST UNIT 1-Part A on THURSDAY, FEB 23