here - Principles of Microeconomics
advertisement

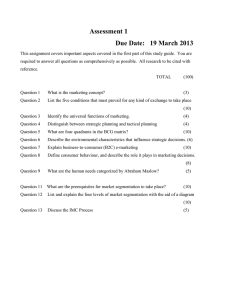
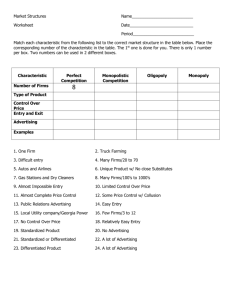
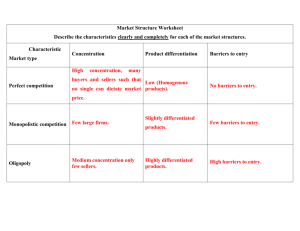
Monopolistic Competition & Oligopoly Principles of Microeconomics Boris Nikolaev Monopolistic Competition • This model was developed independently in the 1930’s by Edward Chamberlin and Joan Robinson. 1. Many sellers 2. Each seller has a small market share 3. Product differentiation some market power some control over price 4. Free or almost free entry 5. Non-price competition (advertising) Examples • • • • • • • • • • • Banks (?) Sporting Goods Radio Stations (?) Fish and Seafood Clothing Jewelry Computers Fast Foods [mac ad] Apparel Stores Canned Goods Convenience Stores Short-Run (profit) Short-run (loss) Notice that as before when ATC > p the firm is making a loss. Long Run Efficiency • Robinson vs Chamberlin • Are chain stores good? Product Differentiation The firm controls (1) price (2) product quality (3) advertisement. 1. Quality [advertisement vs reality] [Mc Donald’s reply] 2. Location / hours of availability 3. Brand names and packaging [Nike] [reebok][reebok 2][Asics] Non-Price Competition • Advertising creates intangible (perceived) value. [watch here] [ads] Brand Names Top 10 Brands [see here] mentioned on Twitter [see here] What top brands spend on advertisement • Microsoft – more than 20 percent of their annual revenue or $11.5 billion • Coca-Cola – more than $2.5 billion • Yahoo – more than 20 percent of their annual revenue or $1.3 billion • eBay – 14 percent to 15 percent of its revenue – which was $871 million, much of that to advertise on Google • Google – In the millions rather than billions of dollars – with $188 million • Starbucks – $95 million Big Pharma Spends More On Advertising Than Research And Development, Study Finds [source] Is advertising good or bad? • Galbraith vs Hayek Oligopoly Characteristics (e.g. TV – Comcast, Viacom, Time Warner, Disney, Fox) 1. A few large sellers (in the case of two duopoly) 2. Homogeneous (e.g. bananas) or differentiated product (e.g. coffee) 3. Market power 4. Mutual interdependence 5. Barriers to entry Examples • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Airlines Auto Industry Steel/ Cement Tobacco Soft Drinks Beer Movie TV (Media) Book Publishing Coffee/ Bananas Cell Phones Air Defense Banking Cereal Oil Duopoly The Prisoner’s dilemma Cartels Examples • • • • • • OPEC DeBeers Caviar NCAA [milk] [gas] Problems Pseudo-variety • Technique oligopolies use to capture bigger share of the market. The way it works: flood the shelves with similar (quality) products but trivially differentiated. • It gives the illusion of variety; yet, it makes real competition harder as new companies now compete with more products as theirs is less noticeable on the shelf. [Bud Ad] [ Bud Ad 2] Is small beautiful… • Or is bigger better?