Rethinking Social Sector at 18th Amendment
advertisement

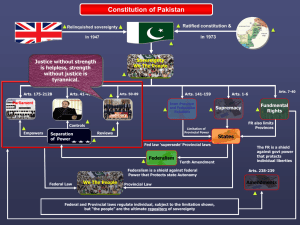
Reclamation of federal democracy through 18th Amendment: Lessons Learnt and Way Forward ZAFARULLAH KHAN WWW.CIVICEDUCATION.ORG Understanding devolution? Decentralization (assigned) versus Devolution (allocated could only be changed through 2/3 majority) Principle of subsidiarity (Nearest tier is the best service provider). Logic for vibrant Local government. Vertical: Federal [Defence and Debt establishment], provincial [space for politics], local/district [political or administrative proxies] Pakistani experience: Centralized GRIP Horizontal: ‘Trias Politica’ [separation of power Legislature (vision, frame-work), Executive (implementation), Judiciary (interpretation, adjudication)] Pakistani experience: Distorted institutional spaces. Indigenized politics amid colonial steal frames Federal Democratic Pyramid Federal Provincial Local What we have is an ‘Inverted Pyramid’ Federal Provincial Local Quest for provincial autonomy Since 1947 Pakistani politics was around the Question of Provincial Autonomy. Partitions (1947) and Dismemberment (1971) on denial of autonomy. Political Struggles/Documents authored in the idiom of autonomy: [21-points of Jugtoo Front, Six points, MRD Declaration, Charter of Democracy all authored in idiom of Provincial Autonomy] ‘A user manual of statecraft’. Lawyer’s Constitution: Legalistic solutions to primarily political questions (Circumvented, convenient, colored versus consensus) When the Constitution is suspended our Fundamental Rights are suspended The chain process Red Card: Country at conflict since 1947, covert war since 1979, overt war since 2001. Disequilibrium in civil-military relations, divided and weak politics [ethnic, religious/sectarian] Green Card: Prelude: Charter of Democracy [May 2006] Election 2008: sustained consensus despite odds Democratic rapprochement: 7th NFC, Aghaaz-e-Haqooq Balochistan, Parliamentary Committee on National Security etc. Cleaning the Constitution: Parliamentary Committee on Constitutional Reforms Operationalizing reforms: Implementation Commission New Constitutional software Indigenous/home grown legislative, administrative and fiscal reforms with political consensus. Re-written Federal-provincial pact (politics in the idiom of provincial autonomy), expanded fundamental rights. Paradigm of Institutional power: the Parliament repository of power. (CCI, NEC, NFC, Committees to appoint judges, Election Commission of Pakistan, Caretakers, NCSW, NCHR). Referendum question in Joint Sitting. Proactive provinces/autonomy: Provincial role in Emergency, Governor to be from the Province, 140-A Local Government by provinces with minimum bench marks. Joint and equal ownership in natural resources, protected share in National Finance Commission. Cooperative Federalism: Metaphor of ‘joint family’ instead of ‘divorce.’ Federalize institutions to nurture federal culture. Chance for cooperative federalism Abolition of Concurrent list (Structural/institutional changes, financial obligations, political consequences). Possibilities for better governance architecture, equality/equity via multi-factor PFC International obligations and indigenous compliance Articles 141-174 (Constitution) deal with relation between federation and provinces. There were seventeen (17) amendments Concept of Residual powers (142-c) Federal List-II (Shared responsibility) Entry 13: Interprovincial coordination and matters Council of Common Interests, National Economic Council, National Finance Commission monitoring. Functionality of CCI Number of CCI Meetings Number of CCI Meetings 8 4 3 3 3 1 Zulfiqar Ali Bhutto 0 Gen. Ziaul Haq 0 Benazir Bhutto Nawaz Sharif Moeen Qureshi 3 1 0 Benazir Bhutto Nawaz Sharif 0 Pervez Shaukat Aziz Yousaf Raza Musharaf Gillani Pervaiz Ashraf Nawaz Sharif Informal communication link Constitutional reports S. no Report Periodicity The Senate of The National Provincial Pakistan Assembly of Assemblies Pakistan 1 Principles of Policy Article 29 (3) Annual Yes Yes th (After the 18 Amendment) 2 Council of Common Interests Article 153 (4) Annual Yes Yes No th th (After the 18 (After the 18 Amendment) Amendment) 3 National Economic Council Article 156 (5) Annual Yes Yes th (After the 18 (After the 18th Amendment) Amendment) 4 National Finance Commission Bi-annual Article 160 (3B) Yes Yes Yes th th (After the 18 (After the 18 (After the 18th Amendment) Amendment) Amendment) Provincial report? 5 Auditor General Article 171 Yes Yes th (After the 18 Amendment) Annual Yes, every province its’ own report Yes, every province its’ own report Compliance! CCI Report NEC Report NFC Report Principles of Policy Last report of 2012-13 laid on June 6, 2014 Last report of 2012-13 laid on Aug. 12, 2014 Last report of July-Dec. 2012 laid on May 7, 2014 Last Report of 2011-12 laid on Aug. 12, 2014 Last reports: 2011-12 2010-11 Last reports 2010-11 Since July-Dec. 2010 (four reports) Combined report of 2008-09 and 2009-10 No discussion in No discussion in No discussion in No discussion in the Senate and the the Senate and the the Senate and the the Senate and the National Assembly National Assembly National Assembly National Assembly Responsible: CCI secretariat: Ministry of IPC has to prepare Responsible: NEC Secretariat: Cabinet Division Responsible: Finance Ministry Responsible: Cabinet Division Policy: Education Contested devolution Creation of Federal Ministry (an issue with CCI) National Curriculum Council? According to Economic Survey of Pakistan 2013-14 In rural Pakistan 74 percent attend public schools, 26 percent private schools including Madrasah In Urban Pakistan 41 percent go to public and 59 percent to private schools including Madrasah Out of 156 Degree Awarding Institutions/Universities 87 [55.76 %] are public and 69 [44.23 %] are private. It is time to re-think EDUCATIONAL GOVERNANCE in Pakistan CREATE FEDERAL CULTURE AND MINDSET Province/Area RTE Legislation Passed Enacted Federal The Right to Free and Compulsory Education Capital Act-2012 Dec. 19, 2012 Dec. 24, 2012 Balochis 1. tan 2. Jan. 28, 2014 Feb. 4, 2014 Jan. 25, 2014 Feb. 3, 2014 The Compulsory Education in the province of Balochistan Act-2014 The Balochistan Introduction of mother languages as compulsory additional subject at Primary level Act-2014 Khyber- The Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Supervision of Pakhtun Curricula, Text Board and Maintenance of khwa Standards of Education Act, 2011 Punjab 1. 2. 3. Sindh The Punjab Curriculum Authority Act-2012 [In September 2014 it has been merged with Punjab Text Book Board] The Punjab Free and Compulsory Education Ordinance 2014 HEC The Sindh Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education Act, 2013 Sindh Higher Education Commission June 21, 2012 Ordinance promulgated The Ordinance’s legal life on May 13, 2014. is 120-day Introduced in the Provincial Assembly on May 16. Feb. 13, 2013 March 6, 2013 April 28, 2014 National Security Purse/Revenues Sindh Revenue Board-2010 Punjab Revenue Authority-2012 Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa Revenue Authority-2013 Provincial powers to raise loans within prescribed limits by the National Economic Council Public Debt and Fiscal Responsibility laws? Resource distribution (7th NFC, Control over natural resources, GST on Services, duties in respect of succession to property, estate duty in respect of property, Capital gains, powers to raise loans etc.) Scenarios within constitutional path Trust the provinces (transfer, transition, transformation) Special Committee of the Senate, Standing Committee of CCI, PM’s special committee Constitutional Amendments (2/3 can bring change) Facilitate transition (Cost of devolution, hand-holding etc.) with better inter-governmental relations, communication and Cooperation Create Federal culture and mindset. Federal filters for policy and planning and establishment of federal institutions instead of the institutions of the federal government. Future governance challenges? First time provinces controlled by different parties. The Senate dominated by the Opposition till March 2015 Pending Population Census since 2008. [Redistribution of economic, political wealth and demand for new provinces] The 8th NFC due in 2015 [Negotiations to start in 2014]. Especially for HEC, Vertical Programs health Amending Article 27 (Quota system) since Aug. 2013 Functionality of federal forums like: the CCI and the NEC Functional Local Government: November 2014 deadline Compatibility of ‘centralized bureaucracy’ with ‘devolved governance. Pending agenda of Civil Services Reforms. Final question? Where are the proactive provinces that were yearning for autonomy?