30-53 can be found in Unit 2
advertisement

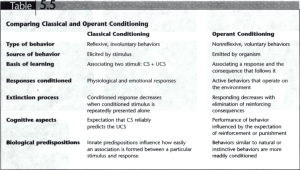
General Psych Final Review ~ 2015 Name:_________________________________ Directions: COMPLETE ALL 115 of these terms for credit toward your 4th Q grade 1. The definition of psychology is: 14. What is a problem associated with archival research? 2. What type of psychologist would explain a person's behavior based on what is happening in the person’s brain? 15. The national census, conducted every 10 years, is an example of which kind of research? 16. Define CASE STUDY: 3. What type of psychologist would be interested in why someone does something in reaction to others or the group? 4. What is primary difference between psychologists and psychiatrists? 5. Define PHRENOLOGY: 17. Define CORRELATION: 18. Define NEGATIVE CORRELATION: 19. Define POSITIVE CORRELATION: 6. Why is the year 1879 so important in the field of psychology? 7. Write a key word or words for each of the perspectives: a. Humanistic = b. Biological (Neuroscience) = c. Cognitive = d. Social/Cultural= e. Behavioral = f. Psychoanalytic = 8. Which perspective rejected psychology's early emphasis on the internal workings of the mind. 9. What is the key issue in psychology that contrasts the heredity with the environment as the major influence on behavior: 10. What is the difference between a theory & a hypothesis? 11. Define OPERATIONALIZE: 20. In correlational research, the strength of the relationship between two variables is indicated by: 21. What is the major problem involved in conducting a correlational study? 22. What does the term experimental manipulation mean? 23. What is the main advantage of experimental research? 24. The subjects in the control group experience all the factors that the subjects in the experimental group are experiencing except: 25. The dependent variable is defined as the factor in a study that: 26. The independent variable in an experiment is defined as the: 27. What was the dependent variable in the Latané and Darley study of bystander helpfulness was: 28. Define CORRELATIONAL COEFFICIENT: 12. Define ARCHIVAL RESEARCH: 13. What are the advantages of using archives? 29. Define PLACEBO: #1-29 can be found in Unit 1 #30-53 can be found in Unit 2 30. Which feature of the neuron makes it distinct as compared to other cells in the body? 55. Define PERCEPTION: 31. Define DENTRITE: 56. Define STIMULUS: 32. Define MYELIN SHEATH: 57. Define ABSOLUTE THRESHOLD: 33. Give an analogy for the function of myelin: 58. Define DIFFERNCE THRESHOLD: 34. Damaged or insufficient myelin sheath would cause the nerve impulse to travel…? 59. Define SENSORY ADAPTATION: 35. The speed of transmission in a neuron will occur fastest if what is true about the myelin sheath around the axon? 36. Define ACTION POTENTIAL: 37. Where are neurotransmitters stored? 38. Define SYNAPSE: #54-68 can be found in Unit 5 39. Too much dopamine? Too little dopamine? 40. Too little SEROTONIN: 60. Define BLIND SPOT: 61. Define AFTERIMAGE: 62. List the receptor pairs in opponent-process theory: 63. Define PHEROMONES: 64. The chemical that transmits pain messages to the brain is known as… 41. Define EEG: 65. According to the gate-control theory of pain, how can the gates that allow for the perception of pain close? 42. Define MRI: 66. Olfactory cells are found in the: 43. Define CEREBRAL CORTEX: 67. Define PERCEPTUAL CONSTANCY. 44. OCCIPITAL LOBE: 68. Define SUBLIMINAL PERCEPTION: 45. TEMPORAL LOBE: 46. FRONTAL LOBE: #69-86 can be found in Unit 2 47. PARIETAL LOBE: 48. DEFINE CEREBELLUM: 49. Define HYPOTHALAMUS: 69. Describe one’s body during REM sleep. 70. During a typical night of sleep, the length of stage 4 sleep _______________, and the length of REM sleep _______________. 71. When people are deprived of REM sleep, they show which of the following behaviors when they can rest without disturbance? 72. Define ALPHA WAVES: 50. Define ASSOCIATION AREAS: 51. What happened to railroad worker Phineas Gage? 52. The language disorder in which speech sounds fluent but makes no sense is: 53. DEFINE neuroplasticity 54. Define SENSATION: 73. Define DELTA WAVES: 74. In a typical night's sleep, the longest dream for most sleepers is most likely to occur: 75. Sleepers are least responsive to outside stimulation during which stage of sleep? 76. The theory that proposed that dreams represent forbidden and unknown desires is the ____________________ theory. 94. In the Little Albert studies (Watson & Rayner, 1920), the conditioned response (CR) was 95. Define EXTINCTION: 77. Define MANIFEST CONTENT of dreams: 96. Define GENERALIZATION: 78. Define LATENT CONTENT of dream: 97. Define SPONTANEOUS RECOVERY: 79. Define ACTIVATION SYNTHESIS Theory of Dreaming: 98. The law of effect states that… 80. Define DREAMS-FOR-SURVIVAL Theory of Dreaming: 99. Who is the psychologist most closely associated with research on operant conditioning? 81. Define UNCONSCIOUS WISH FULFILLMENT Theory of Dreaming: 100. Define THORNDIKE’S PUZZLE BOX: 101. Define SKINNER BOX: 82. What is the primary characteristic of hypnosis? 102. When the probability that a behavior will occur again increases, ______ has occurred. 83. What is ongoing controversy regarding hypnosis? 84. Addictive drugs differ from ordinary medication because they: 85. What do caffeine and cocaine have in common? 86. What is the difference between classical and operant conditioning? #86-110 can 87. In Pavlov's classic studies on classical be found in conditioning, the neutral stimulus (NS) was Unit 6 88. In Pavlov's classic studies on classical conditioning, the unconditioned stimulus (UCS) was 103. A reinforcer is a stimulus that… 104. Define POSITIVE REINFORCEMENT: 105. When a person's behavior increases because an unpleasant stimulus is removed from her environment, then she has experienced a _____. 106. When the probability that a behavior will occur again decreases, _____ has occurred. 107. One advantage of using punishment to change behavior is that punishment … 108. What is a disadvantage of using punishment to change behavior? 89. In Pavlov's classic studies on classical conditioning, the unconditioned response (UCR) was 109. 90. In Pavlov's classic studies on classical conditioning, the conditioned stimulus (CS) was 91. In Pavlov's classic studies on classical #111-115 conditioning, the conditioned response (CR) was can be 92. Watson and Rayner's (1920) research usingfound Little Albert was important for showing that… in Unit 7 93. In the Little Albert studies (Watson & Rayner, 1920), the conditioned stimulus (CS) was Define SHAPING: 110. Define OBSERVATIONAL LEARNING: 111. DEFINE ENCODING: 112. Define PROCEDURAL MEMORY: 113. Define EPISODIC MEMORY: 114. Describe the difference between IMPLICIT & EXPLICIT MEMORY: 115. Define FLASHBULB MEMORY: