Study guides for Huffman's chapters 1 and 2
advertisement

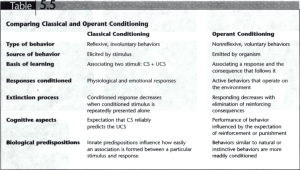
Chapter 4 1. What’s the difference between sensation & perception? Name the 3 processes of each 2. For each sense (vision, audition, gustation, olfaction, the skin senses, vestibular and kinesthetic senses): a) identify the stimulus; b) name the receptors and the structure/s where they are located; and c) identify the sensation. 3. Compare and contrast rods and cones. 4. Explain the trichromatic and the opponent-process theories of color perception. 5. What part of the ear is involved in balance and feeling dizzy? 6. Describe how early life experiences, expectation, personal motivations and context affect perception. Compare bottom-up versus top-down perception. 7. Summarize criticisms of studies claiming ESP. What are some of the reasons we believe in ESP? 8. Compare & contrast the map of the body on the somatosensory strip with our actual physical bodies. What is different, and why? Chapter 5 1. What are circadian rhythms? 2. Identify the two stages of wakefulness and the 5 stages of sleep. Describe the EEG wave pattern associated with each of these stages. 3. In which stages does dreaming occur? Identify the physical and physiological changes that occur during REM sleep. 4. Describe the sequence of stages of a typical night’s sleep, including the length of the sleep cycles. 5. Name two factors that affect species-specific sleep patterns. 6. Describe the repair/restoration theory of sleep. 7. Describe activation-synthesis hypothesis and cognitive view of why we dream 8. What is the difference between dyssomnias and parasomnias? 9. What is insomnia? sleep apnea? narcolepsy? 10. When do nightmares, night terrors, sleepwalking and sleeptalking occur during sleep? At what ages are they more commonly experienced? 11. Define psychoactive drug, drug abuse, tolerance and withdrawal symptoms. What is the difference between psychological and physical dependence? 12. What are the 4 major drug groups? For each, indicate: a) examples of drugs; b) drug effects; and c) whether or not dependence results. Chapter 6 1. Define learning. Compare & contrast classical vs. operant conditioning. 2. Describe how classical conditioning occurs. Define, identify and contrast reflex, neutral stimulus, unconditioned and conditioned stimulus, unconditioned and conditioned response, systematic desensitization, extinction, spontaneous recovery, higher order conditioning, stimulus generalization. 3. Cite a few examples of classical conditioning (CC) in our everyday life. Explain in detail how CC works in these examples, by identifying CS, UCS, UCR and CR. 4. Describe the procedure Watson used to establish fear of the white rat in little Albert. 5. What kinds of responses can be classically conditioned? Familiarize yourself with the role CC plays in the establishment of prejudice and phobias, in medical treatments, and in advertisements. 6. Define and distinguish positive and negative reinforcement, positive and negative punishment, escape, avoidance, shaping. 7. Describe how punishment can result in increased aggression, avoidance behavior, modeling and learned helplessness. 8. Describe how superstitions can be learned by means of operant conditioning. 9. What characterizes observational learning? (Modeling is another word for observational learning). Describe how observational learning is involved in prejudice, media influences, and aggressiveness. Chapter 12 1. Define motivation and emotion. 2. Review the six major theories of motivation. Think about how to apply each of these to explaining someone’s behavior in a real-life example. 3. How does one’s level of arousal influence one’s performance in general? In simple vs. complex tasks? When doing something in front a group that’s a mastered skill vs. a new skill? 4. Contrast intrinsic vs. extrinsic motivation. 5. What are the 3 components of emotion? 6. What’s the difference between a social smile and a Duchenne smile? 7. Describe the 4 major theories of emotion. How would each one explain a given emotional experience? How do arousal and cognition affect emotion in each theory? 8. What is emotional contagion, and how does it work? 9. Describe Schacter and Singer’s classic study. 10. How do polygraphs work? What do they measure? Why shouldn’t we trust them? 11. How are emotional expressions similar and different across cultures? 12. What purpose do emotions serve according to evolutionary theory? What are the basic emotions? 13. What is Maslow’s hierarchy?