Psychology of Learning Exam #1 Study Guide When there is a

Psychology of Learning
Exam #1 Study Guide
When there is a learning experience, but no opportunity to use the learning until later, what has occurred?
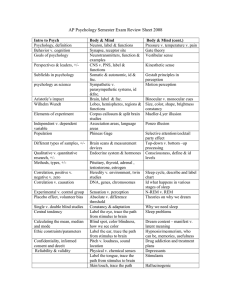
The areas of human function that psychology addresses
How does science relate to psychology?
Random selection/ random assignment
Purpose of having a control group in an experiment
Uses of theory
How do you know if the findings of your experiment were significant
Who needs to sign an informed consent?
Ethical concerns in research
Understand the UCS, CS, UCR, CR (classical conditioning)
Define reflexes
Trace conditioning
The nature of acquisition
Extinction- how do you eliminate the conditioned response?
What kinds of things represent a learned response?
What did the Little Albert experiment show?
What was Watson trying to prove? stimulus generalization vs. stimulus discrimination
Guthrie’s technique used to break a bad habit by presenting a stimulus over and over to eliminate an undesirable response
Guthrie’s’ S-R connection/ the threshold method of breaking a bad habit
Eugenics- how is this legally used?
Systematic Desensitization is like what Guthrie method?
What did Thorndike conclude from his puzzle box experiments?
Could the same activity be satisfying to one person but punishing to another?
Thorndikes’ law of effect was a forerunner of whose later theory?
What is the law of multiple response? Law of response by analogy? Law of set?
Insight/ Readiness/trial and error/ law of exercise/ law of effect
Reinforcers/ annoyers
Associative shifting
The nature of deduction
Dependent vs. independent variables
Emitted vs elicited response
What reinforcement schedule produces the fastest learning?
Positive vs. negative reinforcement
Shaping/ fading
Operants
What’s the advantage of using a Skinner box?
Schedule of reinforcement
The nature of a reinforce
Variable vs. fixed ratio schedule
Discrimination/ counterconditioning