Chapter3 Learning A relatively permanent change in behavior caused
advertisement
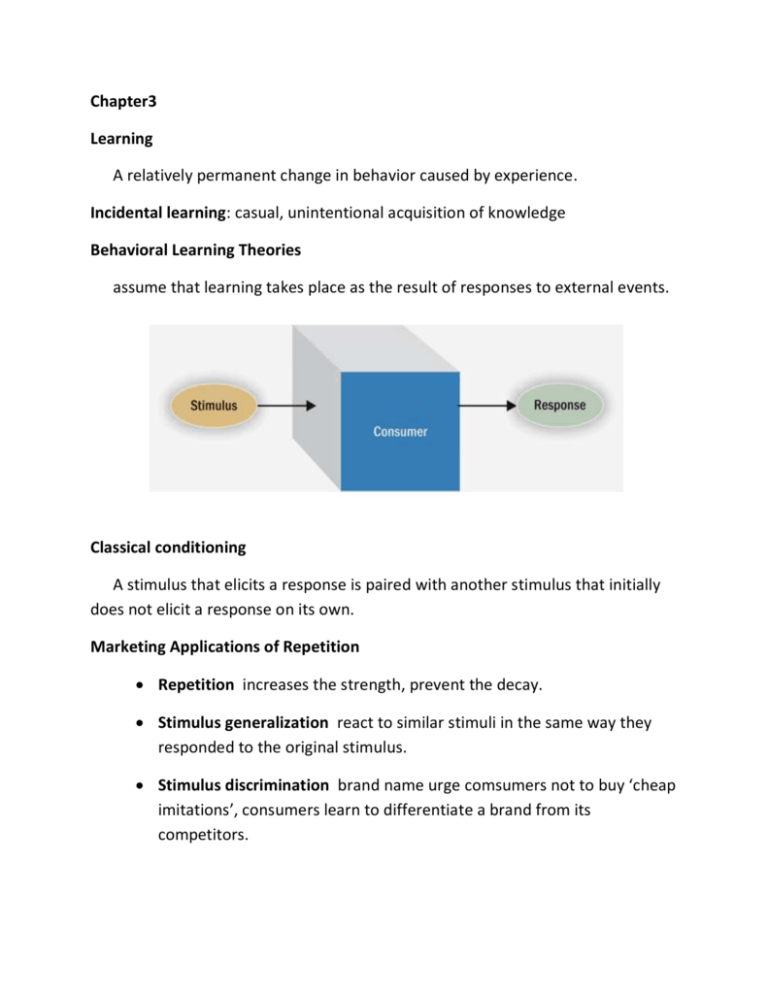
Chapter3 Learning A relatively permanent change in behavior caused by experience. Incidental learning: casual, unintentional acquisition of knowledge Behavioral Learning Theories assume that learning takes place as the result of responses to external events. Classical conditioning A stimulus that elicits a response is paired with another stimulus that initially does not elicit a response on its own. Marketing Applications of Repetition Repetition increases the strength, prevent the decay. Stimulus generalization react to similar stimuli in the same way they responded to the original stimulus. Stimulus discrimination brand name urge comsumers not to buy ‘cheap imitations’, consumers learn to differentiate a brand from its competitors. Marketing applications of stimulus generalization • Family branding • Product line extensions • Licensing • Look-alike packaging Instrumental Conditioning The individual learns to perform behaviors that produce positive outcomes and to avoid those that yield negative outcomes. Instrumental conditions occurs in one of these ways: • Positive reinforcement • Negative reinforcement • Punishment • Extinction Marketing applications of Instrumental Conditioning principles Frequency marketing: rewards regular purchases prize, get better as they spend more Cognitive Learning Theories Consumers is a complex-problem solvers People will actively use information from the world around them to master their environment. Observational Learning Learn when watch actions so it will be available when we need. The memory process Memory Systems











