AP Psychology Semester Exam Review Sheet 2008
advertisement
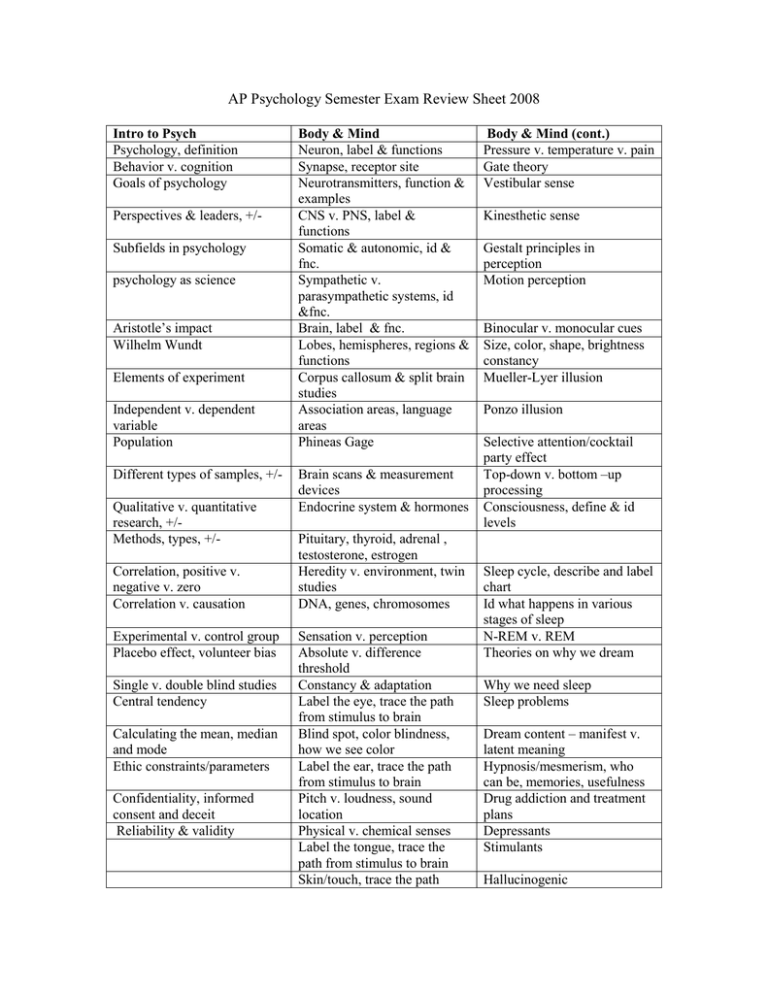
AP Psychology Semester Exam Review Sheet 2008 Intro to Psych Psychology, definition Behavior v. cognition Goals of psychology Perspectives & leaders, +/Subfields in psychology psychology as science Aristotle’s impact Wilhelm Wundt Elements of experiment Independent v. dependent variable Population Different types of samples, +/Qualitative v. quantitative research, +/Methods, types, +/Correlation, positive v. negative v. zero Correlation v. causation Experimental v. control group Placebo effect, volunteer bias Single v. double blind studies Central tendency Calculating the mean, median and mode Ethic constraints/parameters Confidentiality, informed consent and deceit Reliability & validity Body & Mind Neuron, label & functions Synapse, receptor site Neurotransmitters, function & examples CNS v. PNS, label & functions Somatic & autonomic, id & fnc. Sympathetic v. parasympathetic systems, id &fnc. Brain, label & fnc. Lobes, hemispheres, regions & functions Corpus callosum & split brain studies Association areas, language areas Phineas Gage Brain scans & measurement devices Endocrine system & hormones Pituitary, thyroid, adrenal , testosterone, estrogen Heredity v. environment, twin studies DNA, genes, chromosomes Sensation v. perception Absolute v. difference threshold Constancy & adaptation Label the eye, trace the path from stimulus to brain Blind spot, color blindness, how we see color Label the ear, trace the path from stimulus to brain Pitch v. loudness, sound location Physical v. chemical senses Label the tongue, trace the path from stimulus to brain Skin/touch, trace the path Body & Mind (cont.) Pressure v. temperature v. pain Gate theory Vestibular sense Kinesthetic sense Gestalt principles in perception Motion perception Binocular v. monocular cues Size, color, shape, brightness constancy Mueller-Lyer illusion Ponzo illusion Selective attention/cocktail party effect Top-down v. bottom –up processing Consciousness, define & id levels Sleep cycle, describe and label chart Id what happens in various stages of sleep N-REM v. REM Theories on why we dream Why we need sleep Sleep problems Dream content – manifest v. latent meaning Hypnosis/mesmerism, who can be, memories, usefulness Drug addiction and treatment plans Depressants Stimulants Hallucinogenic Learning & Cognition Classical conditioning, association Pavlov’s study Stimulus & response UCS v. CS & UCR v. CR Experiment identification and creation Taste aversion Extinction Spontaneous recovery Generalization & discrimination Treatment uses Little Albert Operant conditioning, reinforcement Primary v. secondary reinforcers Positive v. negative reinforcement Negative reinforcement v. punishment Continuous v. partial reinforcement, ex. Ratio v. interval reinforcement schedules, ex. Which schedule is best for quick learning? Long term? Shaping Latent learning Observational learning Bandura’s Bobo doll Episodic v. semantic v. implicit memory Encoding, storing & retrieving Codes: visual, acoustic, semantic, +/Maintenance v. elaborate rehearsal Context-dependent retrieval State-dependent retrieval Tip-of-the-tongue phenomenon Sensory, short-term & longterm memory Learning & Cognition (cont) Chunking, magic number Primacy, recency Interference Long-term memory capacity Forgetting Recognition, recall & relearning Infantile, Retrograde & anterograde amnesia Memory improvement skills Mnemonics Loftus research & memory construction Social Cognition/Interaction Attitude Cognitive anchor Persuasion Central & Peripheral route 2 sided argument Emotional appeal Sales resistance Prejudice Discrimination Scapegoat Social perception Primacy & recency effect Attribution theory Actor observer bias Fundamental attribution error Self-serving bias Attraction Triangular model of love Intimacy/passion/commitment Social facilitation Social loafing Diffusion of responsibility Group polarization Leadership styles Norms Altruism Bystander effect Foot-in-the-door Door-in-the-face









![IV. LOCAL FOOD POLICY ORGANIZATIONS [F-6, F-7, F-8, & F-9]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/014124515_1-8b088a2bd293dea68992c5199d52d0b7-300x300.png)
