Nuclear Radiation
advertisement

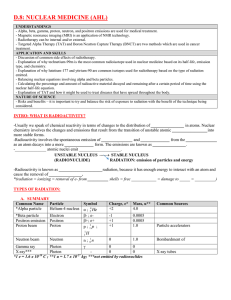
Warm Up What is nuclear radiation? Unit Test Thursday 2/3/2014 Nuclear Radiation Video Marie Curie, Nobel Prize Winner What is Radioactivity? When nuclei of unstable isotopes gain stability by undergoing changes These reactions: are called nuclear reactions are always accompanied by the emission of large amounts of energy are spontaneous are not affected by changes in temp, pressure, or presence of catalysts cannot be slowed down, speeded up, or turned off The process by which atoms emit rays is called radioactive decay OR nuclear decay Unstable nucleus = can be due to the overall size of the nucleus, having too many or too few neutrons Eventually, unstable radioisotopes of one element are transformed into stable, nonradioactive isotopes of a different element 3 Types of Radiation Alpha particles—positive charge, consists of helium nuclei (two protons & two neutrons) Beta particles—negative charge, consists of fast-moving electrons formed by the decomposition of a neutron in an atom Gamma rays—no charge, is high energy electromagnetic radiation given off by a radioisotope, have no mass, emission of these rays does not alter the atomic number or mass of an atom Penetrating Ability Example Uranium-238 releases alpha radiation Is transformed into another radioisotope, thorium-234 Example Carbon-14 emits a beta particle as it undergoes nuclear decay, transforming into nitrogen-14 A neutron decomposes into a proton! Example Gamma rays are often emitted along with alpha or beta Cobalt-60 shown below Collaborative Group Work Create a study tool: On a separate sheet of paper, create a graphic organizer to compare the three types of radiation. You should include: Symbols Charge Relative mass Penetrating power Nuclear Reactions Practice Homework: Finish nuclear reactions practice sheet Begin studying for unit test by visiting the following site to review nuclear radiation: http://www.mdc.edu/kendall/chmphy/nuclear/types.htm You can also watch IsaacsTEACH and review chemistry unit 2 on youtube. Warm Up 2/4/2014 What is the octet rule? How does an atom of sodium adhere to the octet rule? Homework Review Nuclear Fission & Fusion Fusion = when two smaller nuclei combine or fuse Example = hydrogen + hydrogen helium (this occurs in the stars) Fission = when a larger nucleus is split into lighter nuclei Example = atom bomb or nuclear reactors, the splitting of uranium Both types of reactions release large amounts of energy Homework Watch IsaacsTEACH 2.8 on valence electrons and Lewis structures (YouTube video) Take notes on how to write Lewis structures On last week’s homework, add column for Lewis structures & complete Begin to study for your test—review notes, practice problems completed, IsaacsTEACH videos (2.1-2.9) Warm Up 2/5/2014 Use the symbols for and distinguish between alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays. Questions about Unit Test? Periodic Table Mendeleev