Ch 8 part 1
advertisement
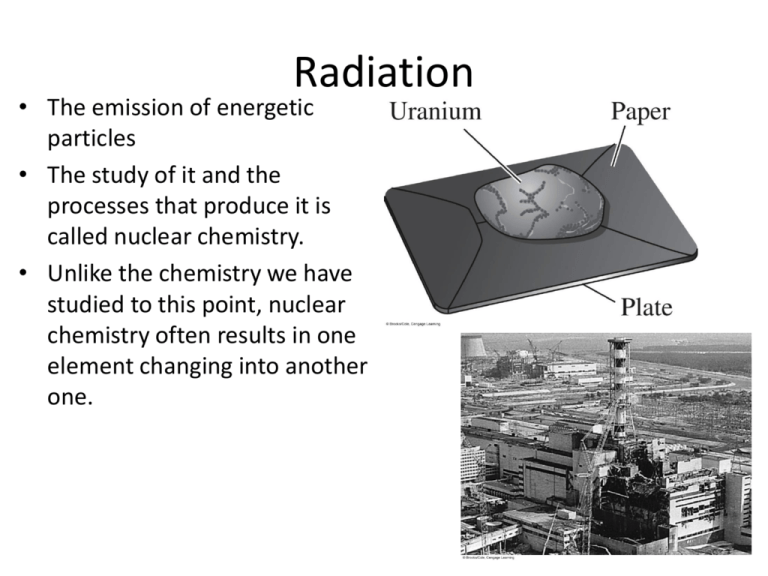
Radiation • The emission of energetic particles • The study of it and the processes that produce it is called nuclear chemistry. • Unlike the chemistry we have studied to this point, nuclear chemistry often results in one element changing into another one. Tragedy • April 26, 1986, 1:24 am • V.I. Lenin nuclear power plant • Chernobyl, USSR • Explosions in reactor 4 • 31 immediate deaths, 230 hospitalizations, countless exposures to high-level radiation • The aftermath continues to this day. Becquerel • Discovered that his paperwrapped photographic plate was exposed by uraniumcontaining crystals. • This disproved his hypothesis linking exposure to UV light with phosphorescence. • But it revealed a brand-new phenomenon that he called the emission of uranic rays. Marie and Pierre Curie • Searched for the elements that produced the uranic rays • Discovered two new emitters of uranic rays; one was a new element (polonium) • Radioactivity not the result of a chemical reaction • Since the rays were not unique to uranium, a new term was proposed: “radioactivity” • Discovered radium as a result of its “extreme radioactivity” Radioactivity • The result of nuclear instability • • • • Alpha Radiation Composed of two protons and two neutrons Represented by the symbol for a helium nucleus High ionizing power Low penetrating power Beta Radiation • • • • An energetic electron represented by the symbol β Smaller than alpha particles, so more penetrating But this also means less ionizing power In beta decay, a neutron converts to a proton, emitting an electron and increasing the atomic number by 1.











