AP Biology Ch 3
advertisement

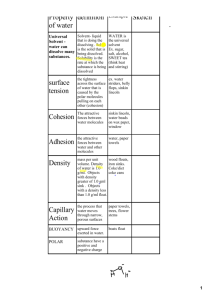
AP Biology Ch 3 - Water 3.1 The Polarity of Water Molecules Results in Hydrogen Bonding • H2O – 2 hydrogen, 1 oxygen • Difference in electronegativity results in polar bonds • Asymmetric shape of molecule results in polar molecule Directions: Cut out your water molecules. Shade the positive side red and the negative side black 3.1 The Polarity of Water Molecules Results in Hydrogen Bonding • Interactions between the positive and negative ends of the molecules are called hydrogen bonds • Molecules of water are constantly moving, hydrogen bonds • 4 emergent properties of water constantly forming and result from hydrogen bonding breaking 3.2 Four Emergent Properties of Water Property 1: Cohesion Explain: Cohesion – Cohesion – Adhesion – Surface tension Importance in Biology (examples): Adhesion 3.2 Four Emergent Properties of Water Property 1: Cohesion Explain: • Cohesion – molecules bond to each other • Adhesion – Molecules bond to another substance • Surface tension – how difficult it is to break the surface of a liquid Importance in Biology: • Water pulled up tree through transpiration (cohesion) • Water held inside plants (adhesion) 3.2 Four Emergent Properties of Water Property 2: Moderation of Temperature Explain: – – – – Kinetic energy Heat vs temperature Specific heat Water as a heat sink Importance in Biology: Water molecules being heated (why does water have a high specific heat?) 3.2 Four Emergent Properties of Water Property 2: Moderation of Temperature • Kinetic energy – energy of motion • Heat – total kinetic energy • Temperature - average kinetic energy y – Example: Swimmer has higher temp, pool has higher heat • Specific heat – amount of heat absorbed to raise temp of 1 g by 10C • Water has such a high specific heat because so much energy goes into breaking the hydrogen bonds 3.2 Four Emergent Properties of Water Property 2: Moderation of Temperature Importance in Biology: • Large bodies of water – cool during the day, warm at night • Stable ocean temps • Regulate the temp of • Organism’s bodies made of everything around them – water – prevents extreme prevent extreme fluctuations fluctuations 3.2 Four Emergent Properties of Water Property 3: Insulation by Ice Explain: Water as a liquid – water density as liquid vs solid – Hydrogen bonding as a liquid vs a solid Importance in Biology: Water as solid 3.2 Four Emergent Properties of Water Property 3: Insulation by Ice • Water is one of a few substances that is less dense as a solid • As molecules slow down and get closer together, hydrogen bonding results in crystalline lattice Importance in Biology: • Cold bodies of water freeze over top, not from the bottom up • Insulates water below, protecting life 3.2 Four Emergent Properties of Water Property 4: Solvent of Life Explain: – – – – – solvent, solute Aqueous solution Hydration shell What will dissolve in water? Hydrophobic vs hydrophilic Importance in Biology: Hydration shell Property 4: Solvent of Life Explain: – solvent, solute - Solute dissolves in solvent – Aqueous solution – water is the solvent – Hydration shell – water molecules surround solute particles because of charges and separate them – What will dissolve in water? – Ionic compounds, polar molecules – Hydrophobic (affinity for water) vs hydrophilic (repel water) 3.2 Four Emergent Properties of Water Property 4: Solvent of Life Importance in Biology: • Allows chemical reactions that sustain life! • Membranes composed of hydrophobic molecules allow internal environment to be different than external environment