Chapter 4 Section 4 Unique Properties of Water
advertisement

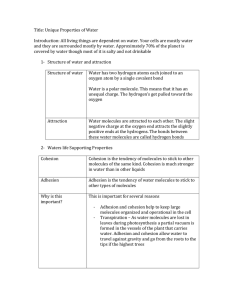
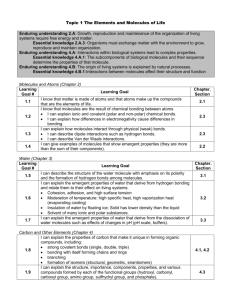
Chapter 4 Section 4 Unique Properties of Water Mrs. Kerstetter Biology Structure of Water All living things are dependent on water Cells are surrounded by fluid that is mostly water Cells are 70-95% water Formula for water? H2O H atoms are joined to O atoms by a single covalent bond Key to water’s unusual properties: 1. 2. 3. Electrons of each covalent bond are not shared equally between the H & O atoms Oxygen has a stronger attraction The unequal sharing causes the Oxygen to have a slightly negative (-) charge, while the hydrogen ends have a slightly positive (+) charge Polarity A molecule in which opposite ends have opposite electrical charges is called a POLAR molecule Water is a polar molecule How are water molecules attracted to each other? Slightly negative O attracts the slightly positive hydrogen of adjacent molecules, causing molecules to become arranged using hydrogen bonds Water’s Unique Properties 1. 2. 3. 4. Cohesion and Adhesion Temperature Moderation Low Density of Ice Ability to Dissolve Other Substances Cohesion and Adhesion Cohesion tendancy of molecules of the same kind to stick to one another Much stronger for water than other liquids Adhesion Attraction between unlike molecules Important to keep large groups of molecules organized in living world Temperature Moderation Thermal energy Total amt of E associated with the random movement of atoms and molecules in a sample of matter Temperature Measure of the average E of random motion of particles in a substance Is temperature transferred from warmer to cooler or cooler to warmer? Warmer to cooler Temperature Moderation Temperature rises bc the molecules move faster In water, some of the E goes to break bonds, so doesn’t heat as fast When you cool a substance the molecules slow and temp drops BUT In water, it forms H bonds, so doesn’t cool as much as a metal Examples of Temp Moderation of Water Oceans and lakes moderate the temperature of nearby land masses El Nino Evaporation and sweat Low Density of Ice Formula for ice? Water is more dense than ice Why? Hydrogen bonds Longer lived bc slower moving than liquid form Why is this important to living things? Ability to Dissolve Other Substances Solution Solute Substance that is dissolved and present in a lesser amount salt Solvent Uniform mixture of 2 or more substances Salt water Substance that dissolves the other substance and is present in a greater amount water Aqueous solution When chemical dissolved in water Main Solvent Water is the main solvent in all cells and in plant sap Polar molecules are easily broken down by water