CNS Meninges
advertisement

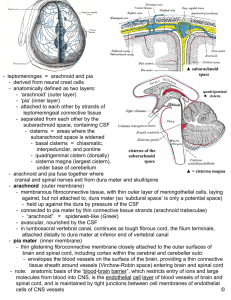
Dr. Nimir Dr. Safaa Ojectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid spaces. Locate the principal subarachnoid cisterns, and arachnoid granulations. Meninges of Brain The brain and spinal cord are surrounded by three protective membranes, or meninges: Dura mater. Arachnoid mater. Pia mater. The dura mater of the brain has two layers: Endosteal layer. Meningeal layer . These are closely united except along certain lines, where they separate to form venous sinuses. Endosteal layer covers the inner surface of the skull bones. At the sutures, it is continuous with the sutural ligaments. At the foramen magnum, it does not become continuous with the dura mater of the spinal cord. The meningeal layer is the dura mater proper. It is a dense fibrous membrane covering the brain and is continuous through the foramen magnum with the dura mater of the spinal cord. It provides tubular sheaths for the cranial nerves as they pass through the foramina in the skull. Outside the skull, the sheaths fuse with the epineurium of the nerves. In vertebral canal there is an epidural space containing fat and internal vertebral venou plexus. The meningeal layer sends inward four septa(falx cerebri,falx cerebelli,tentorium cerebelli & diaphragma sellae). The function of these septa is to restrict the displacement of the brain associated with acceleration and deceleration, when the head is moved. The dura is innervated by trigeminal, vagus, first three cervical spinal nerves and sympathetics. The falx cerebri is a sickle- shaped fold of dura mater that lies in the midline between the two cerebral hemispheres . Narrow anterior end is attached to the internal frontal crest and the crista galli. Broad posterior part blends in the midline with the upper surface of the tentorium cerebelli. The superior sagittal sinus runs in its upper fixed margin, the inferior sagittal sinus runs in its lower concave free margin, and the straight sinus runs along its attachment to the tentorium cerebelli. The tentorium cerebelli is a crescent-shaped fold of dura mater that roofs over the posterior cranial fossa. It covers the upper surface of the cerebellum It has is a gap, tentorial notch, for the passage of the midbrain. The fixed border forms transverse & superior petrosal sinuses . Falx cerebelli is between the two cerebellar hemispheres. It contains the occipital sinus. Diaphragma sellae roofs sella turcica. Arachnoid mater is a delicate, impermeable membrane covering the brain and lying between the pia mater internally and the dura mater externally. It is separated from the dura by a potential subdural space, filled by a film of fluid. It is separated from the pia by subarachnoid space, which is filled with cerebrospinal fluid. Arachnoid and pia in some spaces are widely separated to form the subarachnoid cisternae. Cisterna cerebellomedullaris lies between cerebellum and roof of the fourth ventricle. Cisterna interpeduncularis lies between the two cerebral peduncles. In certain areas, arachnoid projects into the venous sinuses to form arachnoid villi (arachnoid villi ) through which cerebrospinal fluid diffuses into the bloodstream. Meninges of Spinal Cord Dura mater encloses spinal cord and the cauda equina It is continuous above through the foramen magnum with meningeal layer of brain. Inferiorly, it ends on the filum terminale at lower border of S2. The dura is separated from vertebral canal by extradural space which contains loose areolar tissue and internal vertebral venous plexus. The dura extends along each nerve root and becomes continuous with epineurium. Arachnoid covers spinal cord and lies between the pia mater and dura mater. It is separated from the pia mater by subarachnoid space filled with cerebrospinal fluid. It ends on the filum terminale at the level of S2. Pia mater closely covers spinal cord and thickened on either to form ligamentum denticulatum, which adheres to arachnoid and dura. Prolongation of pia mater, filum terminale attaches to posterior surface of coccyx.