File
advertisement

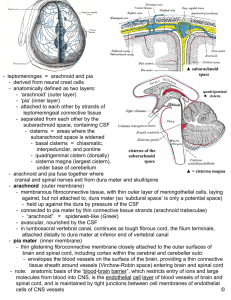
Name : Lungile Ngema Student Number : 50585746 Lesson Plan : Micro lecture 1_Anatomy Target Group : Second year student at Unisa, for Education and Training as a nurse (General, Psychiatry and Community) and Midwifery, Leading to Registration (425, 22 February 1985, as amended) Subject : Anatomy Theme : Meningitis Topic : The microscopic of the brain and the spinal cord Introduction Media : Picture of a house Media : A house offers protection to its entire inhabitant. The roof, walls, windows with burglar bars safeguard the people and the household contents. If one or more of these means of protection is damaged, the inhabitants are at risk of personal harm just as the skull and the meninges protect the brain and spinal cord and any invasion of the meninges threatens the safety of brain functioning. Media : Board (write topic on board: Meninges) OUTCOMES Media : Transparency After this lecture, the students should be able to 1. Identify the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. 2. Describe the dura mater ASSESSMENT OF PRIOR KNOWLEDGE MEDIA : CHART_BRAIN AND SPINAL CORD Q : Name the principal parts of the brain A : Cerebellum, Diencephalon and the brain stem Q : Name the fluid that protects the brain and the spinal cord A : Cerebrospinal fluid Q : Describe how cerebrospinal fluid protects the brain and spinal cord A : The fluid serves as a shock absorbing medium to protect the brain and spinal cord from jolts that would otherwise cause them to crash against the bony walls of the cranial and vertebral cavities Content Media : Writing board DEFINITION : Meninges: meninges are fibrous connective tissues that cover the brain and the spinal cord The meninges provide protection, support and nourishment to the brain and spinal cord. The layers of the meninges are the dura meter, arachnoids and pia mater DURA MATER The outer erring is called the dura mater, meaning tough mother. It is tough, thick, inelastic fibrous and gray. The cranial dura mater consists of 2 layers. The thicker outer layer (periosteal layer) tightly adheres to the cranial bones and serves as perosteum. The inner layer (meningeal layer) forms the true external covering of the brain. The cranial dura mater (meningeal layer) corresponds with the spinal dura mater. The spinal dura mater forms a tube from the level of the second sacral vertebra, where it is fused with filumterminale to the foramen magnum; from here it is continuous with the dura mater of the brain. The subdural space is between the dura mater of the brain. The subdural space is between the dura mater and the arachnoids Q : Name the 3 meninges A : Dura mater, Arachnoid, Pia mater Q : What are the functions of meninges? A : They provide protection; support and nourishment to the brain and spinal cord. Q : Name the space between dura mater and the arachnoid layer. A : Subdural space During the next session I will discuss the arachnoid and the pia mater Summary Media : Transparency, chart, look at outcomes Definition : The meninges are fibrous connective tissue that covers the brain and the spinal cord. They provide protection, support and the nourishment to the brain and the spinal cord. These are 3 layers meninges: dura mater, arachnoid and the pia mater. The dura mater is the outer covering which is tough, thick, inelastic, fibrous and gray. The meningeal layer of the cranial dura mater corresponds with, and is continuous with the spinal dura mater Sources: Smeltzer, S 8c Bare, B. 2000. Brunner 8c Suddarth’s text book of medical-surgical nursing. Nettina, SM. (ed). 2001. The Lippincott Manual of nursing practice. 7th edition. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams 8c Wilkins. Clinical Neurology for students. 2004. Cape Town: UCT COMMENTS - Stick to the meninges not functions