The Spinal Cord
advertisement
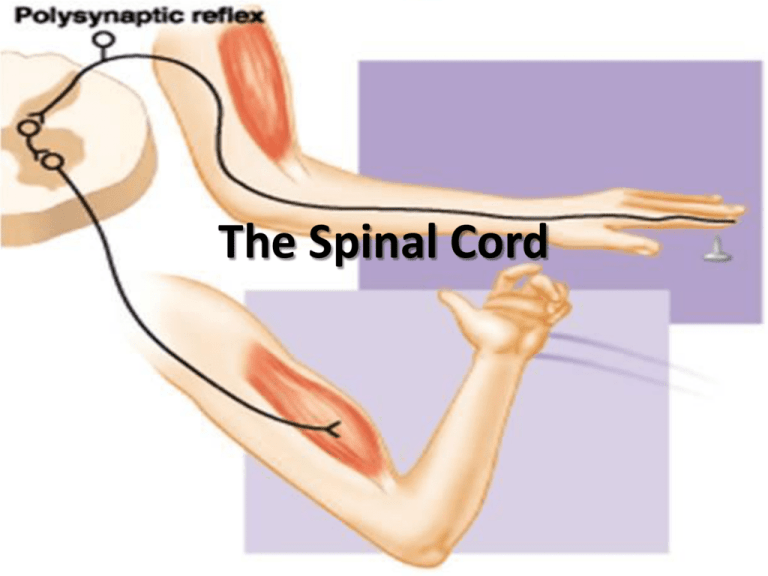
The Spinal Cord Protection Vertebrae Spinal meninges • Three layers of connective tissue – Dura mater – Arachnoid mater – Pia mater • Continuous with cranial meninges Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Spinal Meninges • Epidural space: between vertebrae and dura mater • Dura mater- tough, dense connective tissue • Arachnoid mater: resembles spider’s web – Extends into subarachnoid space • Subarachnoid space – CSF circulates in this space • Pia mater: thin, delicate layer – Adheres to surface of spinal cord (and brain) – Contains blood vessels Spinal Meninges Spinal Meninges Structure of the Spinal Cord Structure of the Spinal Cord Spinal Nerves Nerves attached to spinal cord by 2 roots • Dorsal root: made of axons of sensory neurons – Dorsal root ganglion: swelling containing cell bodies of sensory neurons • Ventral root: composed of axons of motor neurons – Both somatic motor and autonomic motor Spinal Cord Functions Pathways for nerve impulses within tracts • Ascending (sensory) • Descending (motor) Reflexes: fast, involuntary sequences of actions in response to stimuli • Can be simple (withdrawal) or complex (learned sequence such as driving car) The Reflex Arc 1. Sensory receptor: responds to stimulus 2. Sensory neuron: through dorsal root ganglion and root posterior horn 3. Integrating center: single synapse between sensory and motor neurons 4. Motor neuron: from anterior horn ventral root spinal nerve 5. Effector: muscle or gland responds The Reflex Arc











