the MENINGES - mmartinscience
advertisement

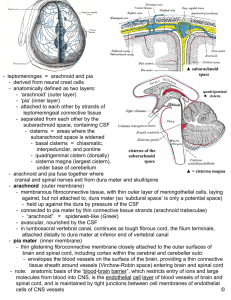
MENINGES
the
The middle layer of the meninges is the arachnoid
delicate
connective
appearance,
Beneath the arachnoid
meninges
are continuous
with the meninges of
in an earlier plate but with several dis-
tinguisk·,g features. In this plate, we examine the unique features
and relate them to f1Jnctions performed by each meninx.
by
Begin
coloring the main title The Meninges. Then, as
the arachnoid
Between the trabeculae
with oxygen
arachnoid
in the subarachnoid
and
Extending
brospinal
nutrients
and
i
0',
f.
.c':
.
'
I
J
, ·11\.
,
--'.'
t"
"!ing its position.
meninx is the dura mater (C). This cov-
~NQ
Y1C€
layers, an outer layer (C1l, also called
it is fused to the periosteum of the cralayer (C2). As the diagram
r;,
ou,'.
fbiu
'i',i'"
kn
cl''''·'l'1~iiilms
1 ji"'f,
oF'
ve'
""r:
';'.'
shows, the
separate to form a gap containing tissue
One of the large vessels is the large vein
(';
';.ifJ·jd
((3).
Veins leading from the brain tissue
")' "inuses, which then lead to the jugular
~ f( ,ughrhe neck. At certain points, the inner dura
mCl'r"'-'JSenas 1m) the fissure dividing the right and left hemisph\·no~ .:J ,.hE. cei'ebrum. This extension or fold of tissue is the falx
cerel}!'i {(<<\!, Other extensions are found near the cerebella and
neO!
1;,6
spacr;
floor of the brain.
the $ubdural
Beneath the dura mater is a small
space (01, which separates
it from the
nexi'
'W'f
:lOW
concentrate
~(;rw of ib detaiis.
~n the second meninx and note
This second layer tends to be the
mos, ctl'1lplex of the layers because cerebrospinal
here.
m
":,0 exchange
cerebrospinal
of fingerlike
fluid percolating
the arachnoid
through
the subarachnoid
villus, then passes
down
space
into the blood
from the brain tissue. This is the
third meninx. This innermost layer is attached to the
brain. As you read about the layer, locate it in the dia-
blues, and
be used to highlight the skull bone (Bl,
'1..TUllo.!
The
We finish with the plate by paying brief attention to the
These arrows may be col-
colors such as greens,
(Iy)
products.
where they are
with the outer layer of the head, and note the posic,t<1iF fA) A medium color may be used here. A
"
waste
into the dural sinus are a number
gram and color it with a light color.
The last of the meninges
!THc'\,
remove
second method by which fluid leaves the brain.
Light colors are recommended since many of
the structures are detailed.
Also, watch for arrows
tio'
are a
extensions of the arachnoid called arachnoid villi. An arachnoid
villus (E2) is indicated in the plate and drawn in detail. The cere-
bU'1d.
We
space
layer itself has no blood vessels.
vessel, which leads it away
with darker
is filled
series of blood vessels (Fl),These vessels supply the brain tissues
meninges and their details. As you read about the three
m0 ;'1Ce, below, color their titles, then locate and color
pointing out specific regions.
diagrams
lation as we shall see momentarily.
enters
th", st;'UC1'T8Sin any of the diagrams
The fibers are
(E1). The detailed
fluid. The fluid will return to the venous circu-
you look over the plate, note the closeup views of the
n
into compartments.
trabeculae
show their structure, The space between the trabeculae
that supplies nutrients and oxygen to the brain and
The. cmnial
area called
the space
with cerebrospinal
the spind cord examined
is a substantial
fibers separating
ion the
during violent contact with the surrounding bones.
They also interface with the cerebrospinal fluid, a type of plasspinal cxd 'issues and removes their metabolic waste products.
(E). It is a
of its spiderlike
space (F), Within this space are a number of
called
Euid
because
the subarachnoid
The meninges supply protection and support for the brain tissues and carry many important vessels between them. They cush-
malike
tissue so named
fluid
Many blood vessels are
between the circulatory
fluid occurs here.
adheres
brain
is the pia mater
(G). This layer
to the surface of the brain and follows its contours as the
folds in at the gyri and
Astrocytes
anchor
forms its fissures called
sulci.
the pia mater to the brain tissue. There are
many blood vessels within the pia mater and the major cerebral
blood vessels lie on top of it within the subarachnoid
the arachnoid.
Beneath the pia mater is the cerebral
tissue may be colored in the diagram
light color is recommended
avoid obscuring
its details.
space below
cortex (H). This brain
to complete the plate. A
since it is detailed,
and it is best to
(2
D
E
F
1_
F1
G
Scalp
Skull bone
Dura mater
Outer layer
A
B
C]
0
0
0
0
Inner layer
(2
0
Dural sinus
(3
0
Falx cerebri
C4
0
D
E
E]
0
0
0
E2
0
Subarachnoid space
Blood vessels
F
0
0
Pia mater
Cerebral cortex
G
Subdural space
Arachnoid
Arachnoid trabeculae
Arachnoid villus
(
F]
H
G
0
0
115