Central Nervous System - Riverside Preparatory High School
advertisement
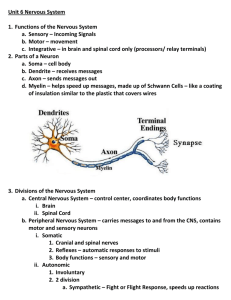
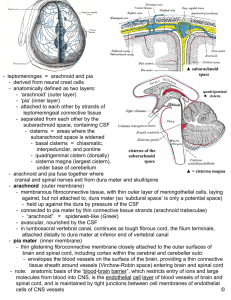
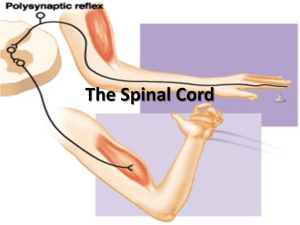
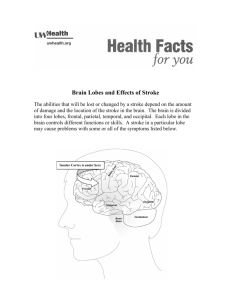
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM MENINGES • Three separate layers of tissue that surround the brain and spinal cord • Provide physical stability and shock absorption • Heavily vascularized • Dura mater • Arachnoid mater • Pia mater DURA MATER • Dura: “tough” • Outermost meninge layer • Fused to bone, in some places extends into cranial cavity forming dural folds • When surrounding spinal cord, not fused to any bone • Epidural space: space between dura mater and walls of vertebral canal • Epidural block: injection of anesthetic into epidural space (epidural during childbirth) ARACHNOID MATER • Space between arachnoid and dura is called subdural space, filled with lymphatic fluid to reduce friction • Subarachnoid space: filled with CSF (shock absorption, transport) PIA MATER • • • • Separated from arachnoid by subarachnoid space Bound to neural tissue Blood vessels fill this layer Supplies the same amount of blood to 3.1 pounds of brain as 61.6 pounds of muscle takes SPINAL CORD • Functions as a highway for nerves going towards and away from the brain • Integrates spinal reflexes • Approximately 18 inches long, about half an inch wide • Mostly decreases in diameter the closer it gets to the sacrum (2 exceptions) • Cervical enlargement: supplies nerves to the shoulder girdle and upper limbs • Lumbar enlargement: provides innervation to the pelvis and lower limbs SPINAL CORD • Central canal: internal passageway filled with CSF • 31 segments: each segment associated with dorsal root ganglia (cell bodies for sensory neurons) • Ventral roots: motor neurons • Dorsal and ventral roots leave at intervertebral foramen • Spinal nerves are classified as mixed (combination of sensory and motor) • Cauda equina: ventral and dorsal roots inferior to the tip of the cord seen in gross dissection BRAIN • Made up of the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, temporal lobe • Roughly 35 billion neurons (roughly 98% of neural tissue in the body) • Average weight in an adult is ~pounds • Males are generally 10% larger brain mass • Females show no lower performance in cognition despite size difference MAJOR DIVISIONS OF THE BRAIN • Cerebrum • Divided into cerebral hemispheres (location of conscious thought, memory, and complex movements) • Diencephalon • Made up of thalamus (relay and processing centers for sensory info), hypothalamus (emotions, autonomic function, hormone production), pituitary (hormone production), and epithalamus (hormone production) MAJOR DIVISIONS OF THE BRAIN • Brain stem: processing centers and relay stations • Midbrain (process visual and auditory info), pons (connects cerebrum to brainstem, somatic and visceral motor control), medulla oblongata (sensory info to thalamus, major centers for autonomic function: HR, BP, resp, digestion) • Cerebellum: voluntary and involuntary motor function, fine motor control ACTIVITY • Draw and color a picture of the central nervous system. • Label the following structures: cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, cerebellum, frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, occipital lobe • Under each structure, give a basic function of them