MACROMOLECULES JIGSAW.doc
advertisement

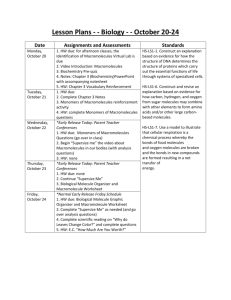
MACROMOLECULES JIGSAW- DIGESTION INTRODUCTION Macromolecules are large, complex organic molecules mostly made up of C and H, sometimes N, S and P. They are the raw materials that our body needs to provide energy and perform all cellular functions. These macromolecules are also known as _______________ because they are made of many _______________ (or building ______________) strung together. Analogy: _____________are to ______________ as ______________ are to ________________ Task: In group of 4, gather information about structures, functions and examples of the class of macromolecule you're assigned. Once done, teach what you got to your group members FOUR types of macromolecules: 1. Carbohydrates Structure Function Examples Function Examples a. Monosaccharides: b. Disaccharides c. Polysaccharides: 2. LIPIDS Structure 3. PROTEINS Structure Function Examples 4. NUCLEIC ACIDS Structure Function Examples ENZYMES: are ________________ that _______________ biochemical reactions such as hydrolysis. Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction in which ____________breaks macromolecules into their _________________. Proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids all need to be broken down by ___________________________ before the body can use them Enzyme names tend to be named after the substances they break down or form and end in ____________ Type of Enzyme Carbohydrase Macromolecule it Breaks Down Carbohydrate Products of Breakdown Simple sugars Lipase Lipid Glycerol and fatty acids Protein Amino acids Nucleic Acid Nucleotides Protease Nuclease Example of Enzyme and Where it Functions Amylase: produce in the salivary glands and functions in the mouth Pancreatic lipase: produced in the pancreas and functions in the small intestine Pepsin produced by stomach glands functions in the stomach Pancreatic nuclease: produced in the pancreasand functions in the small intestine Digestive system overview- Intro NUTRITION HW Read pages 396 - 405 and answer the following questions on a separate sheet. 1. What is a nutrient? 2. Define the terms metabolism, catabolism and anabolism. 3. What factors does metabolic rate depend on? Describe the general difference in energy needs between males and females and why. 4. a) What metric unit is used to measure energy? b) What are calories and how does it relate to 4 a)? 6. How much water is recommended you drink each day? 7. What are vitamins? Give examples. 8. What are minerals? 1 13 2 14 3 15 4 16 5 17 6 18 7 19 8 20 9 21 10 22 11 23 12 24 Label: Activate your prior knowledge and identify the organs of the human digestive system. Digestive system labelling key: